This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print...
Explanation of Sketches Communicating with TWELITE
- 1: Acquire and Control Data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App
- 1.1: Acquire and Control Data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App
- 1.2: Acquire and Control Data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App
- 1.3: Acquire and Control Data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App
- 2: Retrieve Data from Queue App
- 2.1: Get Data from the Queue App
- 2.2: Acquiring Data from the Queue App
- 2.3: Retrieve Data from Queue App
- 3: Retrieve Data from the ARIA App
1 - Acquire and Control Data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App
monitor_spot_app_twelite that retrieves and displays data from the Extremely Simple! Standard Appmonitor_spot_app_twelite that retrieves and displays data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App (App_Twelite). At the end, we will make a modification to operate the output port of the remote device.1.1 - Acquire and Control Data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App
monitor_spot_app_twelite that acquires and displays data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App (App_Twelite). At the end, we will make modifications to operate the output port of the remote device.Location of the Sample Sketch
If you have installed the MWings library, you can open the sketch from Arduino IDE’s File -> Examples -> MWings -> TWELITE SPOT -> Receive -> monitor_spot_app_twelite.
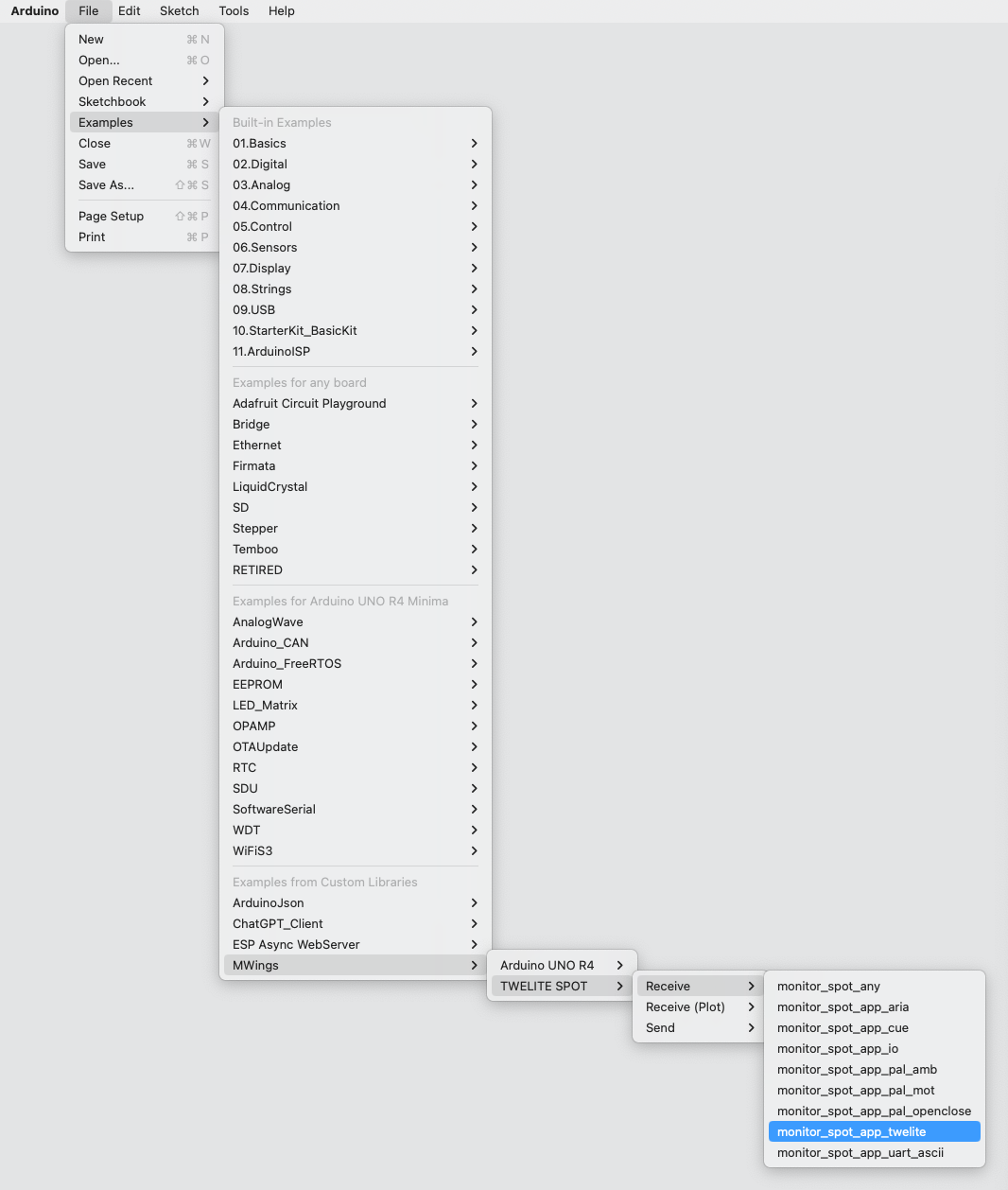
Example of the location display
Sketch
Below is the main source code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from App_Twelite
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const int8_t RX1_PIN = 16;
const int8_t TX1_PIN = 17;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1, RX1_PIN, TX1_PIN);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_Twelite
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
Including the Library
Line 4 includes the MWings library.
#include "MWings.h"
Pin Number Definitions
Lines 6-11 define the pin numbers.
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const int8_t RX1_PIN = 16;
const int8_t TX1_PIN = 17;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
RST_PIN | Pin number connected to the RST pin of TWELITE |
PRG_PIN | Pin number connected to the PRG pin of TWELITE |
LED_PIN | Pin number connected to the ESP32 onboard LED |
RX1_PIN | Pin number connected to the RX1 pin of TWELITE |
TX1_PIN | Pin number connected to the TX1 pin of TWELITE |
TWELITE Configuration Definitions
Lines 13-14 define the settings applied to the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
TWE_CHANNEL | Frequency channel of TWELITE |
TWE_APP_ID | Application ID of TWELITE |
Serial Port Setup
Lines 19-21 initialize the serial ports used and output a startup message to the serial monitor.
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1, RX1_PIN, TX1_PIN);
Serial is used for communication with the Arduino IDE serial monitor. The baud rate is set to 115200 bps to match the serial monitor settings.
On the other hand, Serial2 is used for communication with the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT. The baud rate is also set to 115200 bps to match the initial setting of the TWELITE parent device.
TWELITE Configuration
Lines 24-27 call Twelite.begin() to set up and start the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
Registering Packet Reception Event
Lines 29-49 call Twelite.on() to register the process to perform on received data.
Here, the contents of the received packet are output to the serial monitor.
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
});
The above event is called only when a packet is received from the Extremely Simple! Standard App.
The contents of the received packet are stored in the argument packet of type ParsedAppTwelitePacket.
Message Contents
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
Packet Timestamp | Packet timestamp |
Source Logical ID | Logical device ID of the sending TWELITE |
LQI | Wireless communication quality (0–255) |
Supply Voltage | Power supply voltage (mV) |
Digital Input | Digital input state |
Analog Input | Analog input state |
Updating TWELITE Data
Line 55 calls Twelite.update().
Twelite.update();
Operating the Remote Output Port
Let’s not only acquire the input port state of the Extremely Simple! Standard App but also operate its output port.
Here, based on the LQI (wireless communication quality) when the TWELITE SPOT receives data, we will try to light up the digital output port of the remote device when it approaches the TWELITE SPOT.
Sketch Modification
Modification Details
First, add the following code at line 16.
AppTweliteCommand command;
The above code creates an AppTweliteCommand that stores the content of the command to be sent.
Next, add the following code at lines 52-54.
command.u8DestinationLogicalId = packet.u8SourceLogicalId; // LID
command.bDiState[0] = (packet.u8Lqi >= 100) ? true : false; // DI1
Twelite.send(command);
The above code manipulates the AppTweliteCommand and sends the command using Twelite.send().
Here, the logical device ID of the destination is set, and the state of the output port (DO1) is specified.
For details, please refer to the AppTweliteCommand reference.
This completes the sketch modification. Below is the modified code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from and send data to App_Twelite
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const int8_t RX1_PIN = 16;
const int8_t TX1_PIN = 17;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
AppTweliteCommand command;
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1, RX1_PIN, TX1_PIN);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_Twelite
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
command.u8DestinationLogicalId = packet.u8SourceLogicalId; // LID
command.bDiState[0] = (packet.u8Lqi >= 100) ? true : false; // DI1
Twelite.send(command);
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
Operation Check
Connect an LED and a current limiting resistor between the DO1 pin and VCC pin of the TWELITE DIP child device.
When you upload the modified sketch, the LED lights up when the TWELITE DIP approaches the TWELITE SPOT (i.e., when communication quality is good).
1.2 - Acquire and Control Data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App
monitor_spot_app_twelite that acquires and displays data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App (App_Twelite). At the end, we will modify it to control the output port of the remote device.Location of the Sample Sketch
If you have installed the MWings library, you can open the sketch in Arduino IDE from File -> Examples -> MWings -> monitor_spot_app_twelite.
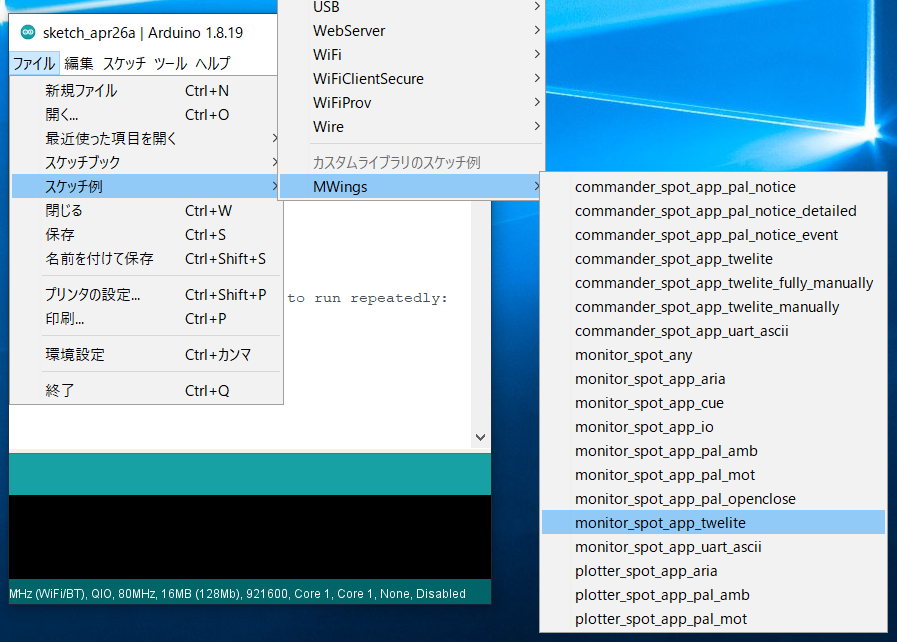
Location
Sketch
Below is the main source code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from App_Twelite
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_Twelite
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
Including the Library
Line 4 includes the MWings library.
#include "MWings.h"
Defining Pin Numbers
Lines 6-8 define the pin numbers.
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
RST_PIN | Pin number connected to the RST pin of TWELITE |
PRG_PIN | Pin number connected to the PRG pin of TWELITE |
LED_PIN | Pin number connected to the ESP32 onboard LED |
Defining TWELITE Settings
Lines 10-11 define the settings applied to the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
TWE_CHANNEL | TWELITE frequency channel |
TWE_APP_ID | TWELITE application ID |
Serial Port Settings
Lines 16-18 initialize the serial ports used and output a startup message to the serial monitor.
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1);
Serial is used for communication with the Arduino IDE’s serial monitor. The baud rate is set to 115200 bps to match the serial monitor settings.
On the other hand, Serial2 is used for communication with the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT. The baud rate is also set to 115200 bps to match the initial settings of the TWELITE parent device.
TWELITE Configuration
Lines 21-23 call Twelite.begin() to configure and start the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
Registering Packet Reception Event
Lines 26-46 call Twelite.on() to register the processing to be done on received data.
Here, the contents of the received packet are output to the serial monitor.
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
});
The above event is called only when a packet is received from the Extremely Simple! Standard App.
The contents of the received packet are stored in the argument packet of type ParsedAppTwelitePacket.
Message Contents
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
Packet Timestamp | Packet timestamp |
Source Logical ID | Logical device ID of the sending TWELITE |
LQI | Wireless communication quality (0–255) |
Supply Voltage | Power supply voltage (mV) |
Digital Input | Digital input state |
Analog Input | Analog input state |
Updating TWELITE Data
Line 52 calls Twelite.update().
Twelite.update();
Controlling the Output Port of the Remote Device
Not only can you acquire the input port state of the Extremely Simple! Standard App, but you can also control the output port of the Extremely Simple! Standard App.
Here, based on the LQI (wireless communication quality) received by the TWELITE SPOT, when the remote device approaches the TWELITE SPOT, the digital output port of the remote device is turned on.
Modifying the Sketch
Modification Details
First, add the following code at line 13.
AppTweliteCommand command;
The above code creates an AppTweliteCommand that stores the content of the command to be sent.
Next, add the following code at lines 49-51.
command.u8DestinationLogicalId = packet.u8SourceLogicalId; // LID
command.bDiState[0] = (packet.u8Lqi >= 100) ? true : false; // DI1
Twelite.send(command);
The above code manipulates AppTweliteCommand and sends the command using Twelite.send().
Here, the logical device ID of the destination is set, and the output port (DO1) state is specified.
For more details, please see the AppTweliteCommand reference.
This completes the modification of the sketch. The modified code is shown below.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from and send data to App_Twelite
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
AppTweliteCommand command;
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_Twelite
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
command.u8DestinationLogicalId = packet.u8SourceLogicalId; // LID
command.bDiState[0] = (packet.u8Lqi >= 100) ? true : false; // DI1
Twelite.send(command);
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
Operation Confirmation
Connect an LED and a current limiting resistor between the DO1 pin and the VCC pin of the child TWELITE DIP.
When you upload the modified sketch, the LED on the TWELITE DIP lights up when it approaches the TWELITE SPOT (i.e., when the communication quality is good).
1.3 - Acquire and Control Data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App
monitor_spot_app_twelite that acquires and displays data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App (App_Twelite). At the end, we will make a modification to control the output ports of the remote device.Location of the Sample Sketch
If you have installed the MWings library, you can open the sketch from Arduino IDE by File -> Examples -> MWings -> TWELITE SPOT -> Receive -> monitor_spot_app_twelite.

Example of the location display
Sketch
Below is the main source code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from App_Twelite
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_Twelite
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
Including the Library
Line 4 includes the MWings library.
#include "MWings.h"
Defining Pin Numbers
Lines 6-8 define the pin numbers.
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
RST_PIN | Pin number connected to the RST pin of TWELITE |
PRG_PIN | Pin number connected to the PRG pin of TWELITE |
LED_PIN | Pin number connected to the ESP32 onboard LED |
Defining TWELITE Settings
Lines 10-11 define the settings applied to the TWELITE master device mounted on TWELITE SPOT.
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
TWE_CHANNEL | TWELITE frequency channel |
TWE_APP_ID | TWELITE application ID |
Setting up Serial Ports
Lines 16-18 initialize the serial ports used and output a startup message to the serial monitor.
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1);
Serial is used for communication with the Arduino IDE serial monitor. The baud rate is set to 115200 bps to match the serial monitor settings.
On the other hand, Serial2 is used for communication with the TWELITE master device mounted on TWELITE SPOT. The baud rate is also set to 115200 bps to match the TWELITE master device’s initial settings.
Configuring TWELITE
Lines 21-23 call Twelite.begin() to configure and start the TWELITE master device mounted on TWELITE SPOT.
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
Registering Event for Packet Reception
Lines 26-46 call Twelite.on() to register the processing to be done when data is sent.
Here, the received packet contents are output to the serial monitor.
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
});
The above event is called only when a packet is received from the Extremely Simple! Standard App.
The received packet contents are stored in the argument packet of type ParsedAppTwelitePacket.
Contents of Messages
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
Packet Timestamp | Packet timestamp |
Source Logical ID | Logical device ID of the sending TWELITE |
LQI | Wireless communication quality (0-255) |
Supply Voltage | Supply voltage (mV) |
Digital Input | Digital input state |
Analog Input | Analog input state |
Updating TWELITE Data
Line 52 calls Twelite.update().
Twelite.update();
Controlling the Remote Output Ports
Let’s not only acquire the state of the input ports of the Extremely Simple! Standard App, but also try controlling its output ports.
Here, based on the LQI (wireless communication quality) when the TWELITE SPOT receives data, we will light up the digital output port of the remote device when it approaches the TWELITE SPOT.
Modifying the Sketch
Modifications
First, add the following code at line 13.
AppTweliteCommand command;
The above code creates an AppTweliteCommand to store the command content to be sent.
Next, add the following code at lines 49-51.
command.u8DestinationLogicalId = packet.u8SourceLogicalId; // LID
command.bDiState[0] = (packet.u8Lqi >= 100) ? true : false; // DI1
Twelite.send(command);
The above code manipulates AppTweliteCommand and sends the command using Twelite.send().
Here, the destination logical device ID is set, and the output port (DO1) state is specified.
For details, see the AppTweliteCommand reference.
This completes the modification of the sketch. The modified code is shown below.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from and send data to App_Twelite
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
AppTweliteCommand command;
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_Twelite
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
command.u8DestinationLogicalId = packet.u8SourceLogicalId; // LID
command.bDiState[0] = (packet.u8Lqi >= 100) ? true : false; // DI1
Twelite.send(command);
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
Operation Confirmation
Connect an LED and a current-limiting resistor between the DO1 pin and the VCC pin of the TWELITE DIP slave device.
When you upload the modified sketch, the LED lights up when the TWELITE DIP approaches the TWELITE SPOT (i.e., when communication quality is good).
2 - Retrieve Data from Queue App
monitor_spot_app_cue that retrieves and displays data from the Queue Appmonitor_spot_app_cue that retrieves and displays data from the Queue App (App_CUE).2.1 - Get Data from the Queue App
monitor_spot_app_cue that obtains and displays data from the Queue App (App_CUE).Location of the Sample Sketch
If you have installed the MWings library, you can open the sketch from Arduino IDE by selecting File -> Examples -> MWings -> TWELITE SPOT -> Receive -> monitor_spot_app_cue.
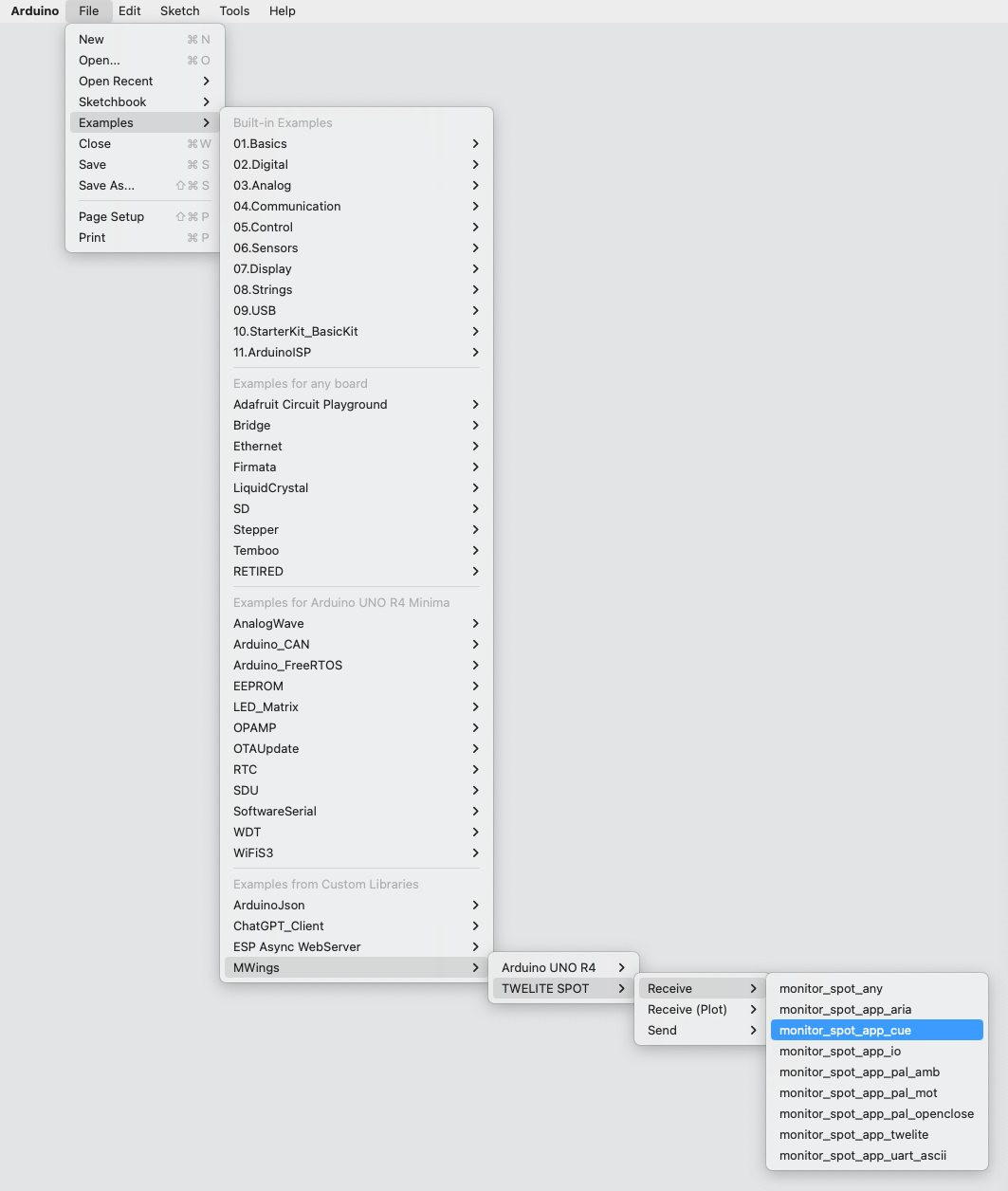
Example of the Save Location Display
Sketch
Below is the source code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from App_CUE (CUE Mode)
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const int8_t RX1_PIN = 16;
const int8_t TX1_PIN = 17;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
void printAccelEvent(const uint8_t event);
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed);
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_CUE (CUE Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1, RX1_PIN, TX1_PIN);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_CUE
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppCuePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Accel Event: ");
printAccelEvent(packet.u8AccelEvent);
Serial.print("Accel X Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesX[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Y Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesY[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Z Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesZ[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
void printAccelEvent(const uint8_t event)
{
switch (event) {
case 0x01: { Serial.print("Dice (1)"); break; }
case 0x02: { Serial.print("Dice (2)"); break; }
case 0x03: { Serial.print("Dice (3)"); break; }
case 0x04: { Serial.print("Dice (4)"); break; }
case 0x05: { Serial.print("Dice (5)"); break; }
case 0x06: { Serial.print("Dice (6)"); break; }
case 0x08: { Serial.print("Shake"); break; }
case 0x10: { Serial.print("Move"); break; }
default: break;
}
Serial.println("");
}
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed)
{
if (changed) {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Leaving or Not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is getting closer"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is getting closer"); break; }
default: break;
}
} else {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is close"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is close"); break; }
default: break;
}
Serial.print(" (Periodic packet)");
}
Serial.println("");
}
Including the Library
Line 4 includes the MWings library.
#include "MWings.h"
Pin Number Definitions
Lines 6-11 define the pin numbers.
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const int8_t RX1_PIN = 16;
const int8_t TX1_PIN = 17;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
RST_PIN | Pin number connected to the TWELITE RST pin |
PRG_PIN | Pin number connected to the TWELITE PRG pin |
LED_PIN | Pin number connected to the ESP32 onboard LED on the board |
RX1_PIN | Pin number connected to the TWELITE RX1 pin |
TX1_PIN | Pin number connected to the TWELITE TX1 pin |
TWELITE Configuration Definitions
Lines 13-14 define the settings applied to the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
TWE_CHANNEL | TWELITE frequency channel |
TWE_APP_ID | TWELITE application ID |
Serial Port Settings
Lines 22-24 initialize the serial ports used and output a startup message to the serial monitor.
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_CUE (CUE Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200);
Serial is used for communication with the Arduino IDE’s serial monitor. The baud rate is set to 115200 bps to match the serial monitor settings.
On the other hand, Serial2 is used for communication with the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT. This also uses a baud rate of 115200 bps to match the initial setting of the TWELITE parent device.
TWELITE Settings
Lines 27-29 call Twelite.begin() to configure and start the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
Registering the Packet Reception Event
Lines 32-52 call Twelite.on() to register the processing to be performed on the received data.
Here, the contents of the received packet are output to the serial monitor.
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppCuePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Accel Event: ");
printAccelEvent(packet.u8AccelEvent);
Serial.print("Accel X Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesX[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Y Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesY[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Z Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesZ[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
The above event is called only when a packet from the Queue App (TWELITE CUE mode) is received.
The contents of the received packet are stored in the argument packet of type ParsedAppCuePacket.
Message Contents
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
Packet Number | Packet sequence number |
Source Logical ID | Logical device ID of the sending TWELITE |
LQI | Wireless communication quality (0–255) |
Supply Voltage | Power supply voltage (mV) |
Accel Event | Accelerometer sensor status |
Accel X Axis | X-axis acceleration (1st sample) |
Accel Y Axis | Y-axis acceleration (1st sample) |
Accel Z Axis | Z-axis acceleration (1st sample) |
Magnet State | Magnetic sensor status |
Accelerometer Sensor Status
The output accelerometer sensor statuses are as follows:
Dice (1)-Dice (6)Detected the dice face (orientation).ShakeDetected a shaking motion.MoveDetected a slow movement.
Magnetic Sensor Status
The output magnetic sensor statuses are as follows:
S-pole is getting closerNewly detected the S pole of a magnet.N-pole is getting closerNewly detected the N pole of a magnet.Leaving or Not foundMagnet not detected.S-pole is close (Periodic packet)Detecting the S pole of a magnet.N-pole is close (Periodic packet)Detecting the N pole of a magnet.Not found (Periodic packet)Magnet not continuously detected (periodic packet).
Updating TWELITE Data
Line 58 calls Twelite.update().
Twelite.update();
2.2 - Acquiring Data from the Queue App
monitor_spot_app_cue that acquires and displays data from the Queue App (App_CUE).Location of the Sample Sketch
If you have installed the MWings library, you can open the sketch from Arduino IDE by navigating to File -> Examples -> MWings -> monitor_spot_app_cue.
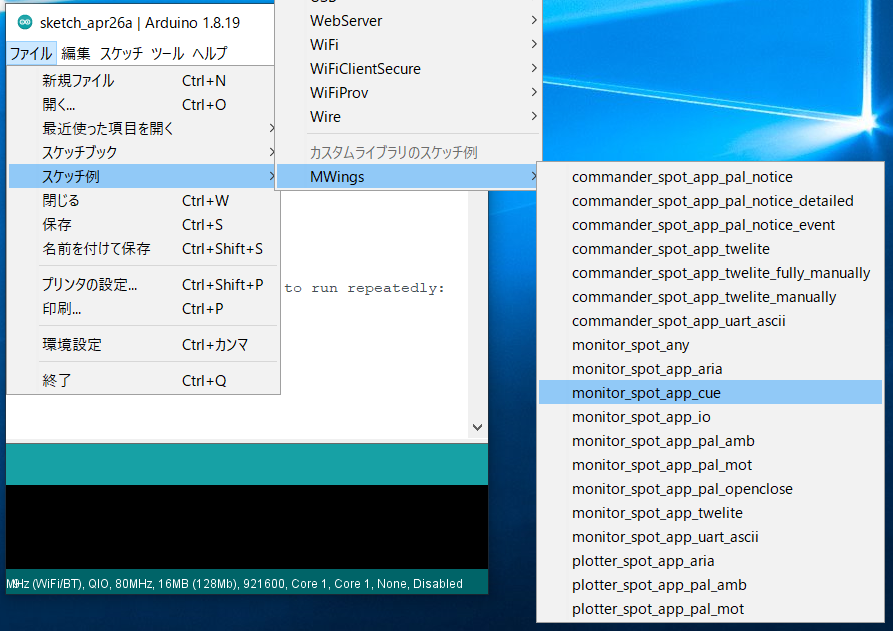
Location
Sketch
Below is the main source code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from App_CUE (CUE Mode)
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
void printAccelEvent(const uint8_t event);
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed);
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_CUE (CUE Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_CUE
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppCuePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Accel Event: ");
printAccelEvent(packet.u8AccelEvent);
Serial.print("Accel X Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesX[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Y Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesY[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Z Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesZ[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
void printAccelEvent(const uint8_t event)
{
switch (event) {
case 0x01: { Serial.print("Dice (1)"); break; }
case 0x02: { Serial.print("Dice (2)"); break; }
case 0x03: { Serial.print("Dice (3)"); break; }
case 0x04: { Serial.print("Dice (4)"); break; }
case 0x05: { Serial.print("Dice (5)"); break; }
case 0x06: { Serial.print("Dice (6)"); break; }
case 0x08: { Serial.print("Shake"); break; }
case 0x10: { Serial.print("Move"); break; }
default: break;
}
Serial.println("");
}
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed)
{
if (changed) {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Leaving or Not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is getting closer"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is getting closer"); break; }
default: break;
}
} else {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is close"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is close"); break; }
default: break;
}
Serial.print(" (Periodic packet)");
}
Serial.println("");
}
Including the Library
Line 4 includes the MWings library.
#include "MWings.h"
Pin Number Definitions
Lines 6-8 define the pin numbers.
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
RST_PIN | Pin number connected to the TWELITE RST pin |
PRG_PIN | Pin number connected to the TWELITE PRG pin |
LED_PIN | Pin number connected to the ESP32 onboard LED |
TWELITE Configuration Definitions
Lines 10-11 define the settings applied to the TWELITE parent device installed on the TWELITE SPOT.
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
TWE_CHANNEL | TWELITE frequency channel |
TWE_APP_ID | TWELITE application ID |
Serial Port Settings
Lines 19-21 initialize the serial ports used and output a startup message to the serial monitor.
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_CUE (CUE Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200);
Serial is used for communication with the Arduino IDE serial monitor. The baud rate is set to 115200 bps to match the serial monitor settings.
On the other hand, Serial2 is used for communication with the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT. This also uses a baud rate of 115200 bps to match the initial TWELITE parent device settings.
TWELITE Settings
Lines 24-26 call Twelite.begin() to configure and start the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
Registering the Packet Reception Event
Lines 29-49 call Twelite.on() to register the processing to be done for the received data.
Here, the contents of the received packet are output to the serial monitor.
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppCuePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Accel Event: ");
printAccelEvent(packet.u8AccelEvent);
Serial.print("Accel X Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesX[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Y Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesY[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Z Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesZ[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
The above event is called only when a packet is received from the Queue App (TWELITE CUE mode).
The contents of the received packet are stored in the argument packet of type ParsedAppCuePacket.
Message Contents
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
Packet Number | Packet sequence number |
Source Logical ID | Logical device ID of the sending TWELITE |
LQI | Wireless communication quality (0–255) |
Supply Voltage | Supply voltage (mV) |
Accel Event | Accelerometer sensor state |
Accel X Axis | X-axis acceleration (1st sample) |
Accel Y Axis | Y-axis acceleration (1st sample) |
Accel Z Axis | Z-axis acceleration (1st sample) |
Magnet State | Magnetic sensor state |
Accelerometer Sensor State
The output accelerometer sensor states are as follows:
Dice (1)-Dice (6): Detected dice face (orientation).Shake: Detected shaking motion.Move: Detected slow movement.
Magnetic Sensor State
The output magnetic sensor states are as follows:
S-pole is getting closer: Newly detected magnetic S-pole.N-pole is getting closer: Newly detected magnetic N-pole.Leaving or Not found: No magnet detected.S-pole is close (Periodic packet): Magnetic S-pole is detected.N-pole is close (Periodic packet): Magnetic N-pole is detected.Not found (Periodic packet): Magnet not detected continuously (periodic packet).
Updating TWELITE Data
Line 55 calls Twelite.update().
Twelite.update();
2.3 - Retrieve Data from Queue App
monitor_spot_app_cue for retrieving and displaying data from the Queue App (App_CUE).Location of the Sample Sketch
If you have installed the MWings library, you can open the sketch from Arduino IDE via File -> Examples -> MWings -> TWELITE SPOT -> Receive -> monitor_spot_app_cue.

Example of the location display
Sketch
Below is the main source code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from App_CUE (CUE Mode)
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
void printAccelEvent(const uint8_t event);
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed);
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_CUE (CUE Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_CUE
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppCuePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Accel Event: ");
printAccelEvent(packet.u8AccelEvent);
Serial.print("Accel X Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesX[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Y Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesY[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Z Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesZ[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
void printAccelEvent(const uint8_t event)
{
switch (event) {
case 0x01: { Serial.print("Dice (1)"); break; }
case 0x02: { Serial.print("Dice (2)"); break; }
case 0x03: { Serial.print("Dice (3)"); break; }
case 0x04: { Serial.print("Dice (4)"); break; }
case 0x05: { Serial.print("Dice (5)"); break; }
case 0x06: { Serial.print("Dice (6)"); break; }
case 0x08: { Serial.print("Shake"); break; }
case 0x10: { Serial.print("Move"); break; }
default: break;
}
Serial.println("");
}
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed)
{
if (changed) {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Leaving or Not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is getting closer"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is getting closer"); break; }
default: break;
}
} else {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is close"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is close"); break; }
default: break;
}
Serial.print(" (Periodic packet)");
}
Serial.println("");
}
Including the Library
Line 4 includes the MWings library.
#include "MWings.h"
Defining Pin Numbers
Lines 6-8 define the pin numbers.
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
RST_PIN | Pin number connected to the RST pin of TWELITE |
PRG_PIN | Pin number connected to the PRG pin of TWELITE |
LED_PIN | Pin number connected to the ESP32 onboard LED |
Defining TWELITE Settings
Lines 10-11 define the settings applied to the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
TWE_CHANNEL | TWELITE frequency channel |
TWE_APP_ID | TWELITE application ID |
Serial Port Setup
Lines 19-21 initialize the serial ports used and output a startup message to the serial monitor.
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_CUE (CUE Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200);
Serial is used for communication with the Arduino IDE serial monitor. The baud rate is set to 115200 bps to match the serial monitor settings.
On the other hand, Serial2 is used for communication with the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT. This is also set to 115200 bps to match the initial settings of the TWELITE parent device.
TWELITE Configuration
Lines 24-26 call Twelite.begin() to configure and start the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
Registering Packet Reception Event
Lines 29-49 call Twelite.on() to register the processing to be performed on the received data.
Here, the contents of the received packet are output to the serial monitor.
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppCuePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Accel Event: ");
printAccelEvent(packet.u8AccelEvent);
Serial.print("Accel X Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesX[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Y Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesY[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Accel Z Axis [0]: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16SamplesZ[0], DEC); Serial.println(" mG");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
The above event is called only when a packet is received from the Queue App (TWELITE CUE Mode).
The contents of the received packet are stored in the argument packet of type ParsedAppCuePacket.
Message Contents
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
Packet Number | Packet sequence number |
Source Logical ID | Logical device ID of the sending TWELITE |
LQI | Wireless communication quality (0-255) |
Supply Voltage | Power supply voltage (mV) |
Accel Event | Accelerometer sensor status |
Accel X Axis | X-axis acceleration (1st sample) |
Accel Y Axis | Y-axis acceleration (1st sample) |
Accel Z Axis | Z-axis acceleration (1st sample) |
Magnet State | Magnetic sensor status |
Accelerometer Sensor Status
The accelerometer sensor status output is as follows:
Dice (1)-Dice (6)Detected dice face (orientation).ShakeDetected shaking movement.MoveDetected slow movement.
Magnetic Sensor Status
The magnetic sensor status output is as follows:
S-pole is getting closerNewly detected S-pole of the magnet.N-pole is getting closerNewly detected N-pole of the magnet.Leaving or Not foundMagnet was not detected.S-pole is close (Periodic packet)Magnet’s S-pole is detected.N-pole is close (Periodic packet)Magnet’s N-pole is detected.Not found (Periodic packet)Magnet has not been continuously detected (periodic packet).
Updating TWELITE Data
Line 55 calls Twelite.update().
Twelite.update();
3 - Retrieve Data from the ARIA App
monitor_spot_app_aria that retrieves and displays data from the ARIA appmonitor_spot_app_aria that retrieves and displays data from the ARIA app (App_ARIA).3.1 - Retrieve Data from Aria App
monitor_spot_app_aria that retrieves and displays data from the Aria App (App_ARIA).Location of the Sample Sketch
If you have installed the MWings library, you can open the sketch from Arduino IDE’s File -> Examples -> MWings -> TWELITE SPOT -> Receive -> monitor_spot_app_aria.

Example of the sketch location display
Sketch
Below is the main source code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from App_ARIA (ARIA Mode)
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const int8_t RX1_PIN = 16;
const int8_t TX1_PIN = 17;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed);
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_ARIA (ARIA Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1, RX1_PIN, TX1_PIN);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_ARIA
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppAriaPacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Air Temperature: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16Temp100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" C");
Serial.print("Relative Humidity: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16Humid100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" %");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed)
{
if (changed) {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Leaving or not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is getting closer"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is getting closer"); break; }
default: break;
}
} else {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is close"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is close"); break; }
default: break;
}
Serial.print(" (Periodic packet)");
}
Serial.println("");
}
Including the Library
Line 4 includes the MWings library.
#include "MWings.h"
Defining Pin Numbers
Lines 6-11 define the pin numbers.
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const int8_t RX1_PIN = 16;
const int8_t TX1_PIN = 17;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
RST_PIN | Pin number connected to the TWELITE RST pin |
PRG_PIN | Pin number connected to the TWELITE PRG pin |
LED_PIN | Pin number connected to the ESP32 onboard LED |
RX1_PIN | Pin number connected to the TWELITE RX1 pin |
TX1_PIN | Pin number connected to the TWELITE TX1 pin |
Defining TWELITE Settings
Lines 13-14 define the settings applied to the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
TWE_CHANNEL | TWELITE frequency channel |
TWE_APP_ID | TWELITE application ID |
Serial Port Setup
Lines 21-23 initialize the serial ports used and output a startup message to the serial monitor.
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_ARIA (ARIA Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1, RX1_PIN, TX1_PIN);
Serial is used for communication with the Arduino IDE serial monitor. The baud rate is set to 115200 bps to match the serial monitor settings.
On the other hand, Serial2 is used for communication with the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT. The baud rate is also set to 115200 bps to match the initial setting of the TWELITE parent device.
TWELITE Configuration
Lines 26-28 call Twelite.begin() to configure and start the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
Registering Packet Reception Event
Lines 31-47 call Twelite.on() to register the processing to perform on the received data.
Here, the content of the received packet is output to the serial monitor.
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppAriaPacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Air Temperature: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16Temp100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" C");
Serial.print("Relative Humidity: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16Humid100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" %");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
The above event is called only when a packet is received from the Aria App (TWELITE ARIA mode).
The contents of the received packet are stored in the argument packet of type ParsedAppAriaPacket.
Message Contents
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
Packet Number | Packet sequence number |
Source Logical ID | Logical device ID of the sending TWELITE |
LQI | Wireless communication quality (0-255) |
Supply Voltage | Supply voltage (mV) |
Air Temperature | Air temperature measured by TWELITE ARIA (°C) |
Relative Humidity | Relative humidity measured by TWELITE ARIA (%) |
Magnet State | Magnetic sensor state |
Magnetic Sensor State
The magnetic sensor states output are as follows:
S-pole is getting closerNewly detected the S pole of the magnet.N-pole is getting closerNewly detected the N pole of the magnet.Leaving or Not foundMagnet was not detected.S-pole is close (Periodic packet)Detecting the S pole of the magnet.N-pole is close (Periodic packet)Detecting the N pole of the magnet.Not found (Periodic packet)Magnet is not continuously detected (periodic packet).
Updating TWELITE Data
Line 53 calls Twelite.update().
Twelite.update();
3.2 - Retrieve Data from ARIA App
monitor_spot_app_aria which receives and displays data from the ARIA App (App_ARIA).Location of the Sample Sketch
If you have installed the MWings library, you can open the sketch from Arduino IDE by navigating to File -> Examples -> MWings -> monitor_spot_app_aria.
Location
Sketch
Below is the main source code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from App_ARIA (ARIA Mode)
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed);
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_ARIA (ARIA Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_ARIA
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppAriaPacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Air Temperature: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16Temp100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" C");
Serial.print("Relative Humidity: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16Humid100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" %");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed)
{
if (changed) {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Leaving or not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is getting closer"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is getting closer"); break; }
default: break;
}
} else {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is close"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is close"); break; }
default: break;
}
Serial.print(" (Periodic packet)");
}
Serial.println("");
}
Including the Library
Line 4 includes the MWings library.
#include "MWings.h"
Pin Number Definitions
Lines 6-8 define the pin numbers.
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
RST_PIN | Pin number connected to the RST pin of TWELITE |
PRG_PIN | Pin number connected to the PRG pin of TWELITE |
LED_PIN | Pin number connected to the ESP32 onboard LED |
TWELITE Configuration Definitions
Lines 10-11 define the settings applied to the TWELITE parent device installed in the TWELITE SPOT.
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
TWE_CHANNEL | Frequency channel of TWELITE |
TWE_APP_ID | Application ID of TWELITE |
Serial Port Settings
Lines 18-20 initialize the serial ports used and output a startup message to the serial monitor.
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_ARIA (ARIA Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1);
Serial is used for communication with the Arduino IDE serial monitor. The baud rate is set to 115200 bps to match the serial monitor settings.
On the other hand, Serial2 is used for communication with the TWELITE parent device installed in the TWELITE SPOT. The baud rate is also set to 115200 bps to match the initial settings of the TWELITE parent device.
TWELITE Settings
Lines 23-25 call Twelite.begin() to configure and start the TWELITE parent device installed in the TWELITE SPOT.
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
Registering Event on Packet Reception
Lines 28-44 call Twelite.on() to register the processing to be performed on the received data.
Here, the contents of the received packet are output to the serial monitor.
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppAriaPacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Air Temperature: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16Temp100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" C");
Serial.print("Relative Humidity: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16Humid100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" %");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
The above event is called only when a packet is received from the ARIA App (TWELITE ARIA mode).
The contents of the received packet are stored in the argument packet of type ParsedAppAriaPacket.
Message Contents
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
Packet Number | Sequential number of the packet |
Source Logical ID | Logical device ID of the sending TWELITE |
LQI | Wireless communication quality (0–255) |
Supply Voltage | Power supply voltage (mV) |
Air Temperature | Temperature measured by TWELITE ARIA (°C) |
Relative Humidity | Relative humidity measured by TWELITE ARIA (%) |
Magnet State | Magnetic sensor status |
Magnetic Sensor Status
The output magnetic sensor states are as follows.
S-pole is getting closerNewly detected magnetic S-pole.N-pole is getting closerNewly detected magnetic N-pole.Leaving or Not foundMagnet not detected.S-pole is close (Periodic packet)Magnetic S-pole detected.N-pole is close (Periodic packet)Magnetic N-pole detected.Not found (Periodic packet)Magnet not continuously detected (periodic transmission packet).
Updating TWELITE Data
Line 50 calls Twelite.update().
Twelite.update();
3.3 - Retrieve Data from ARIA App
monitor_spot_app_aria that retrieves and displays data from the ARIA app (App_ARIA).Location of the Sample Sketch
If you have installed the MWings library, you can open the sketch from Arduino IDE via File -> Examples -> MWings -> TWELITE SPOT -> Receive -> monitor_spot_app_aria.

Example of the location display
Sketch
Below is the main source code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from App_ARIA (ARIA Mode)
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed);
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_ARIA (ARIA Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_ARIA
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppAriaPacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Air Temperature: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16Temp100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" C");
Serial.print("Relative Humidity: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16Humid100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" %");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
void printMagnetState(const uint8_t state, const bool changed)
{
if (changed) {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Leaving or not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is getting closer"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is getting closer"); break; }
default: break;
}
} else {
switch (state) {
case 0x0: { Serial.print("Not found"); break; }
case 0x1: { Serial.print("N-pole is close"); break; }
case 0x2: { Serial.print("S-pole is close"); break; }
default: break;
}
Serial.print(" (Periodic packet)");
}
Serial.println("");
}
Including the Library
Line 4 includes the MWings library.
#include "MWings.h"
Defining Pin Numbers
Lines 6-8 define the pin numbers.
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
RST_PIN | Pin number connected to the RST pin of TWELITE |
PRG_PIN | Pin number connected to the PRG pin of TWELITE |
LED_PIN | Pin number connected to the ESP32 LED on the board |
Defining TWELITE Settings
Lines 10-11 define the settings applied to the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
TWE_CHANNEL | TWELITE frequency channel |
TWE_APP_ID | TWELITE application ID |
Serial Port Settings
Lines 18-20 initialize the serial ports used and output a startup message to the serial monitor.
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_ARIA (ARIA Mode)");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1);
Serial is used for communication with the Arduino IDE’s serial monitor. The baud rate is set to 115200 bps to match the serial monitor settings.
On the other hand, Serial2 is used for communication with the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT. The baud rate is also set to 115200 bps to match the initial settings of the TWELITE parent device.
TWELITE Configuration
Lines 23-25 call Twelite.begin() to configure and start the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
Registering Event on Packet Reception
Lines 28-44 call Twelite.on() to register the processing to be done on received data.
Here, the contents of the received packet are output to the serial monitor.
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppAriaPacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Number: #");
Serial.println(packet.u16SequenceNumber, DEC);
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Air Temperature: ");
Serial.print(packet.i16Temp100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" C");
Serial.print("Relative Humidity: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16Humid100x / 100.0f, 2); Serial.println(" %");
Serial.print("Magnet State: ");
printMagnetState(packet.u8MagnetState, packet.bMagnetStateChanged);
});
The above event is called only when a packet is received from the ARIA app (TWELITE ARIA mode).
The contents of the received packet are stored in the argument packet of type ParsedAppAriaPacket.
Contents of the Messages
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
Packet Number | Packet sequence number |
Source Logical ID | Logical device ID of the sending TWELITE |
LQI | Wireless communication quality (0-255) |
Supply Voltage | Power supply voltage (mV) |
Air Temperature | Temperature measured by TWELITE ARIA (°C) |
Relative Humidity | Relative humidity measured by TWELITE ARIA (%) |
Magnet State | Magnetic sensor state |
Magnetic Sensor State
The magnetic sensor states output are as follows:
S-pole is getting closerNewly detected S pole of the magnet.N-pole is getting closerNewly detected N pole of the magnet.Leaving or Not foundMagnet not detected.S-pole is close (Periodic packet)Magnet’s S pole is detected.N-pole is close (Periodic packet)Magnet’s N pole is detected.Not found (Periodic packet)Magnet not continuously detected (periodic packet).
Updating TWELITE Data
Line 50 calls Twelite.update().
Twelite.update();