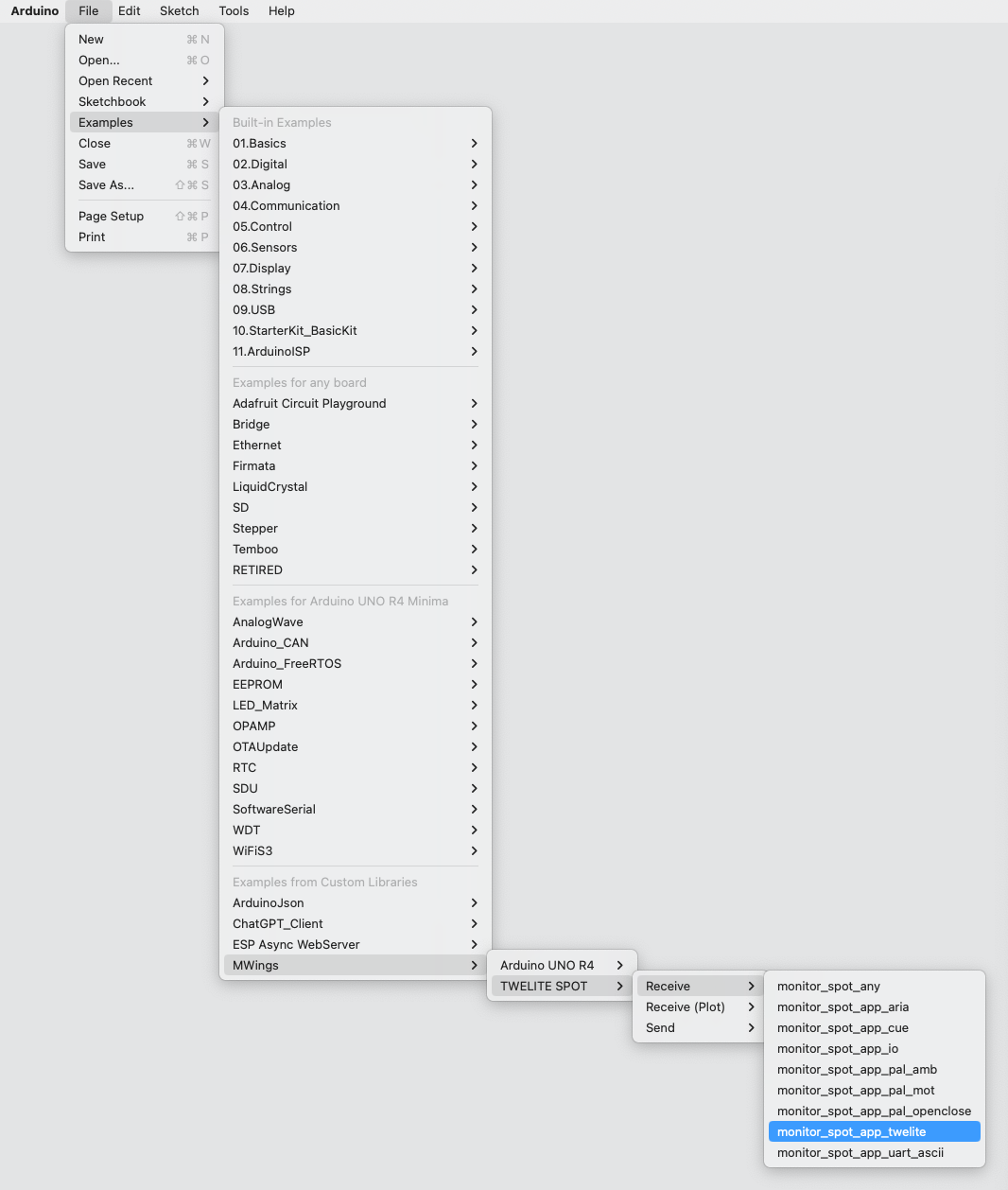
monitor_spot_app_twelite that acquires and displays data from the Extremely Simple! Standard App (App_Twelite). At the end, we will make modifications to operate the output port of the remote device.Location of the Sample Sketch
If you have installed the MWings library, you can open the sketch from Arduino IDE’s File -> Examples -> MWings -> TWELITE SPOT -> Receive -> monitor_spot_app_twelite.
Example of the location display
Sketch
Below is the main source code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from App_Twelite
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const int8_t RX1_PIN = 16;
const int8_t TX1_PIN = 17;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1, RX1_PIN, TX1_PIN);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_Twelite
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
Including the Library
Line 4 includes the MWings library.
#include "MWings.h"
Pin Number Definitions
Lines 6-11 define the pin numbers.
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const int8_t RX1_PIN = 16;
const int8_t TX1_PIN = 17;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
RST_PIN | Pin number connected to the RST pin of TWELITE |
PRG_PIN | Pin number connected to the PRG pin of TWELITE |
LED_PIN | Pin number connected to the ESP32 onboard LED |
RX1_PIN | Pin number connected to the RX1 pin of TWELITE |
TX1_PIN | Pin number connected to the TX1 pin of TWELITE |
TWELITE Configuration Definitions
Lines 13-14 define the settings applied to the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
TWE_CHANNEL | Frequency channel of TWELITE |
TWE_APP_ID | Application ID of TWELITE |
Serial Port Setup
Lines 19-21 initialize the serial ports used and output a startup message to the serial monitor.
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1, RX1_PIN, TX1_PIN);
Serial is used for communication with the Arduino IDE serial monitor. The baud rate is set to 115200 bps to match the serial monitor settings.
On the other hand, Serial2 is used for communication with the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT. The baud rate is also set to 115200 bps to match the initial setting of the TWELITE parent device.
TWELITE Configuration
Lines 24-27 call Twelite.begin() to set up and start the TWELITE parent device mounted on the TWELITE SPOT.
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
Registering Packet Reception Event
Lines 29-49 call Twelite.on() to register the process to perform on received data.
Here, the contents of the received packet are output to the serial monitor.
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
});
The above event is called only when a packet is received from the Extremely Simple! Standard App.
The contents of the received packet are stored in the argument packet of type ParsedAppTwelitePacket.
Message Contents
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
Packet Timestamp | Packet timestamp |
Source Logical ID | Logical device ID of the sending TWELITE |
LQI | Wireless communication quality (0–255) |
Supply Voltage | Power supply voltage (mV) |
Digital Input | Digital input state |
Analog Input | Analog input state |
Updating TWELITE Data
Line 55 calls Twelite.update().
Twelite.update();
Operating the Remote Output Port
Let’s not only acquire the input port state of the Extremely Simple! Standard App but also operate its output port.
Here, based on the LQI (wireless communication quality) when the TWELITE SPOT receives data, we will try to light up the digital output port of the remote device when it approaches the TWELITE SPOT.
Sketch Modification
Modification Details
First, add the following code at line 16.
AppTweliteCommand command;
The above code creates an AppTweliteCommand that stores the content of the command to be sent.
Next, add the following code at lines 52-54.
command.u8DestinationLogicalId = packet.u8SourceLogicalId; // LID
command.bDiState[0] = (packet.u8Lqi >= 100) ? true : false; // DI1
Twelite.send(command);
The above code manipulates the AppTweliteCommand and sends the command using Twelite.send().
Here, the logical device ID of the destination is set, and the state of the output port (DO1) is specified.
For details, please refer to the AppTweliteCommand reference.
This completes the sketch modification. Below is the modified code.
// Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: Receive data from and send data to App_Twelite
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "MWings.h"
const int RST_PIN = 5;
const int PRG_PIN = 4;
const int LED_PIN = 18;
const int8_t RX1_PIN = 16;
const int8_t TX1_PIN = 17;
const uint8_t TWE_CHANNEL = 18;
const uint32_t TWE_APP_ID = 0x67720102;
AppTweliteCommand command;
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial ports
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Monitor example for TWELITE SPOT: App_Twelite");
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1, RX1_PIN, TX1_PIN);
// Initialize TWELITE
Twelite.begin(Serial2,
LED_PIN, RST_PIN, PRG_PIN,
TWE_CHANNEL, TWE_APP_ID);
// Attach an event handler to process packets from App_Twelite
Twelite.on([](const ParsedAppTwelitePacket& packet) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Packet Timestamp: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SequenceNumber / 64.0f, 1); Serial.println(" sec");
Serial.print("Source Logical ID: 0x");
Serial.println(packet.u8SourceLogicalId, HEX);
Serial.print("LQI: ");
Serial.println(packet.u8Lqi, DEC);
Serial.print("Supply Voltage: ");
Serial.print(packet.u16SupplyVoltage, DEC); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Digital Input: ");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[0] ? " DI1:Lo" : " DI1:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[1] ? " DI2:Lo" : " DI2:Hi");
Serial.print(packet.bDiState[2] ? " DI3:Lo" : " DI3:Hi");
Serial.println(packet.bDiState[3] ? " DI4:Lo" : " DI4:Hi");
Serial.print("Analog Input: ");
Serial.print(" AI1:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[0]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI2:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[1]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI3:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[2]); Serial.print(" mV");
Serial.print(" AI4:"); Serial.print(packet.u16AiVoltage[3]); Serial.println(" mV");
command.u8DestinationLogicalId = packet.u8SourceLogicalId; // LID
command.bDiState[0] = (packet.u8Lqi >= 100) ? true : false; // DI1
Twelite.send(command);
});
}
void loop()
{
// Update TWELITE
Twelite.update();
}
Operation Check
Connect an LED and a current limiting resistor between the DO1 pin and VCC pin of the TWELITE DIP child device.
When you upload the modified sketch, the LED lights up when the TWELITE DIP approaches the TWELITE SPOT (i.e., when communication quality is good).