This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print...
How to Write Firmware to ESP32
- 1: How to Write Sketches to ESP32
- 2: How to Write Files to ESP32 (Arduino IDE 1.x)
- 3: How to Upload Files to ESP32 (Arduino IDE 2.x)
- 4: How to Specify the Partition Table for Writing to ESP32
1 - How to Write Sketches to ESP32
Connecting to the Host
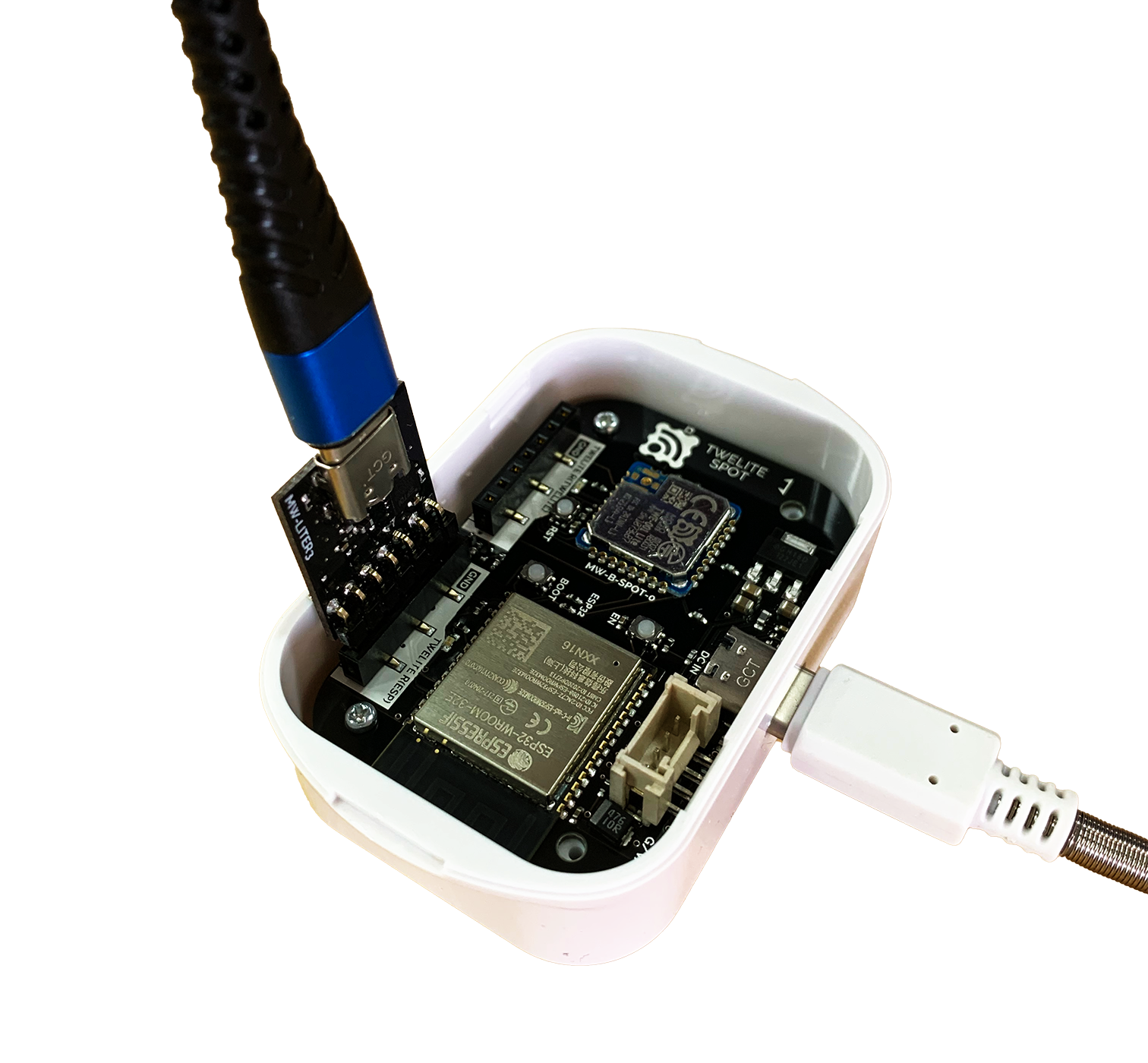
Connect TWELITE R3 / R2
Connect the TWELITE R3 / R2 to the 7P interface (the side labeled ESP32).
Connect Power
Supply 5V power to the USB-C connector on the side.
Connection Example (ESP32)
Operating Arduino IDE
Open the Sketch
Launch the Arduino IDE and open the sketch you want to write.
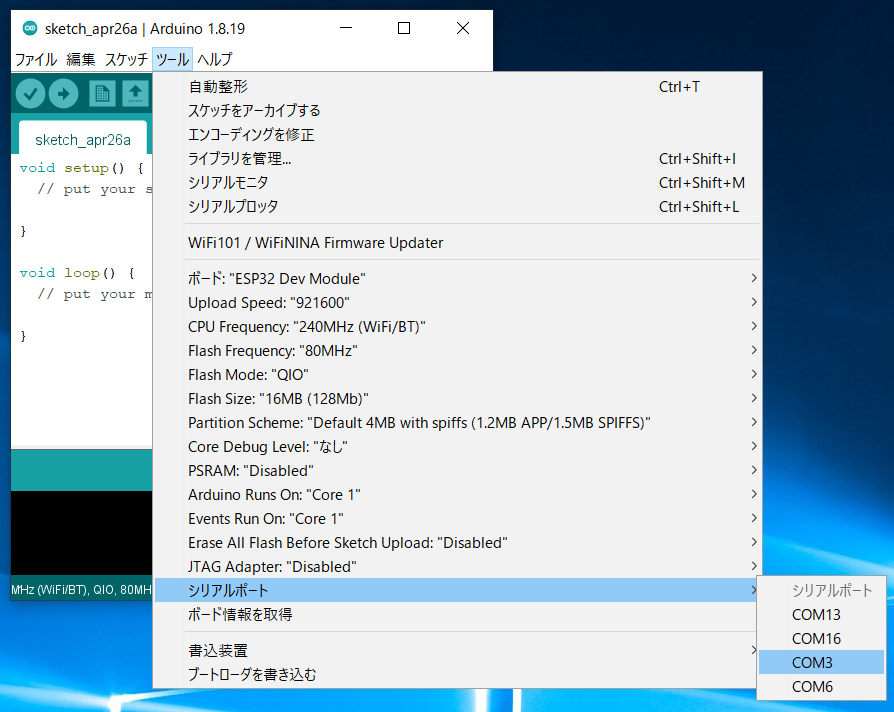
Select the Serial Port
From the Tools -> Serial Port menu, select the port for the TWELITE R3 / R2.
Selecting the Serial Port
COM?, and on macOS/Linux, it will be like /dev/tty?.Start ESP32 in Programming Mode
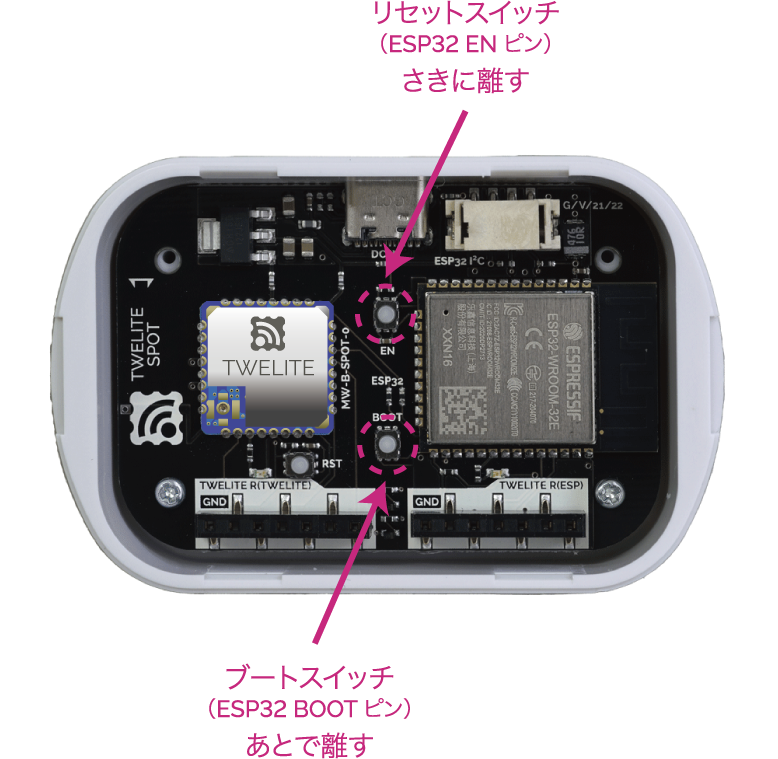
Press the ESP32 reset switch EN(RST) and the ESP32 boot switch BOOT on the TWELITE SPOT, then release them in the order of EN(RST) -> BOOT.
Button Positions
BOOT while resetting, you can enter the ESP32 programming mode.Execute Writing
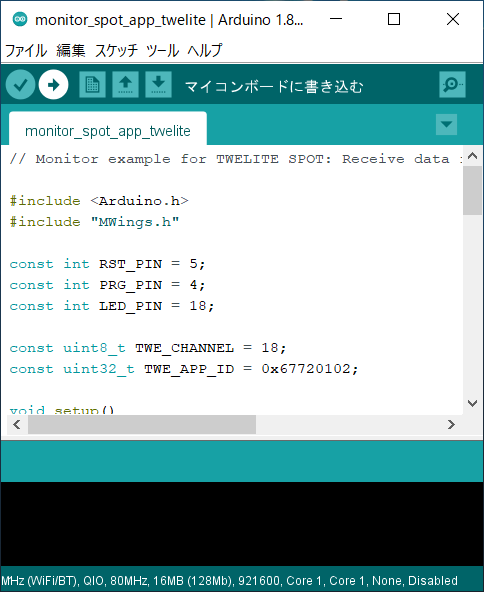
Click the Write to Microcontroller Board button in Arduino IDE.
Write to Microcontroller Board
Hard resetting via RTS pin... will appear at the bottom of the screen.If writing fails and the following message appears, try changing the USB port or USB cable you are using.
A serial exception error occurred: Could not configure port: (6, 'Device not configured')
Reset ESP32
After writing is complete, press and release the ESP32 reset switch EN(RST) on the TWELITE SPOT to reset the ESP32.
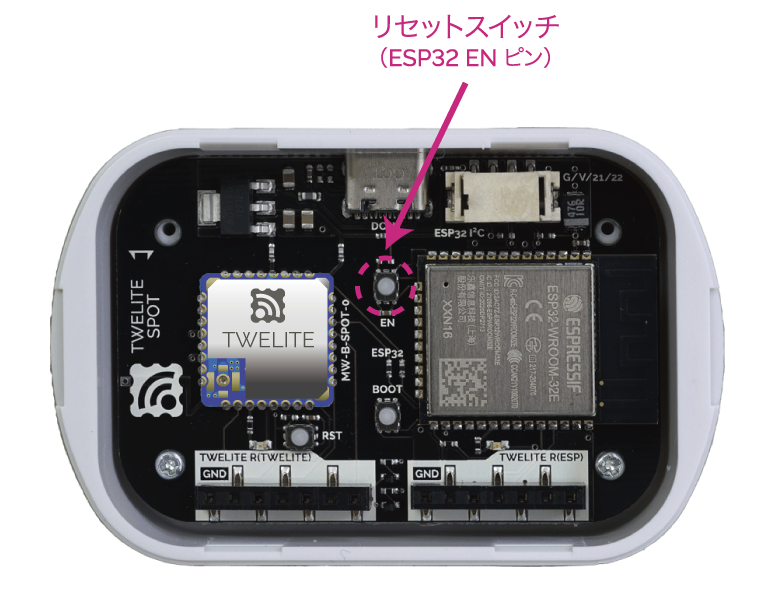

Reset Switch Position
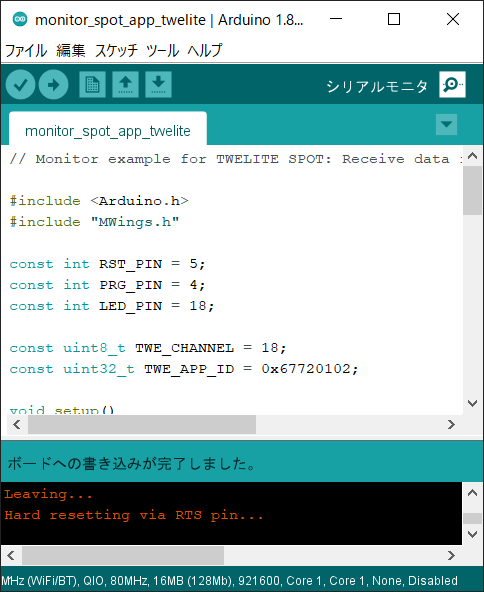
Writing Completion Screen
2 - How to Write Files to ESP32 (Arduino IDE 1.x)
data/ folder) to the ESP32 mounted on TWELITE SPOT.This article introduces an advanced topic (how to treat the flash area of the ESP32 mounted on TWELITE SPOT as a file system and write files such as HTML).
For example, if you do not need to write HTML files to TWELITE SPOT to behave as a web server (implemented in the spot-server sample) or write encryption key files to TWELITE SPOT, you can ignore the contents of this article.
This article uses third-party open-source software.
We cannot provide detailed instructions on third-party software usage. Also, we assume no responsibility for any damages caused by using third-party software.
The method introduced in this article requires Arduino IDE 1.x. Due to technical constraints, as of May 2023, Arduino IDE 2.x is not supported.
Because the plugin used here is written in Java, it does not work with Arduino IDE 2.x, which is not Java-based unlike Arduino IDE 1.x. For more details, see the Arduino IDE GitHub issue (Missing support for external tools / plugins · Issue #58 · arduino/arduino-ide) (in English).
Installing the Plugin
Install the Arduino plugin (arduino-esp32fs-plugin) to write files to the ESP32 flash area.
Downloading the Plugin
Download esp32fs.zip from the following page:
Release Update to support Big Sur · lorol/arduino-esp32fs-plugin
Installing the Plugin
Extract the downloaded
esp32fs.zip.If there is no
toolsfolder in your Arduino sketchbook location (set in Arduino IDE preferences, e.g.,C:\Users\foo\Documents\Arduino), create it.Create the folder
ESP32FS/toolinside thetoolsfolder and place theesp32fs.jarfile extracted from the zip there. (Example path:C:\Users\foo\Documents\Arduino\tools\ESP32FS\tool\esp32fs.jar).The plugin will be available the next time you start Arduino IDE.
Connecting to the Host
Connect TWELITE R3 / R2
Connect TWELITE R3 / R2 to the 7P interface side labeled ESP32.
Connect Power
Supply 5V power to the USB-C connector on the side.

Connection Example (ESP32)
Arduino IDE Operations
Open the Sketch
Start Arduino IDE and open the sketch.
Place Files to Write
Open Sketch -> Show Sketch Folder.
Create a
datafolder at the same level as the sketch file (.ino).Place the files to write inside the
datafolder.
data folder is preserved in the flash area.Select Serial Port
From the Tools -> Port menu, select the port for TWELITE R3 / R2.

Serial Port Selection
COM?, and on macOS/Linux, like /dev/tty?.Boot ESP32 in Programming Mode
Press the ESP32 reset switch EN(RST) and the ESP32 boot switch BOOT on TWELITE SPOT, then release them in the order EN(RST) -> BOOT.

Button Positions
BOOT switches ESP32 into programming mode.Execute Writing
Click Tools -> ESP32 Sketch Data Upload.
At Select FS for
/data folder, select LittleFS.
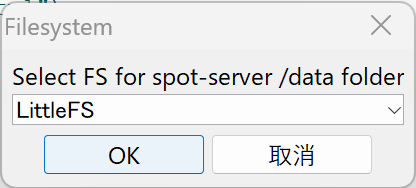
File System Selection Screen
- Click OK.
Hard resetting via RTS pin... is displayed at the bottom of the screen.Depending on your environment, writing may fail with a message like this (confirmed on macOS):
`Error: esptool not found!`
In that case, placing esptool.py in the Arduino15 folder/packages/esp32/tools/esptool_py/<version>/esptool.py might resolve the issue.
For example, on macOS, obtain esptool.py and create a symbolic link as follows:
/usr/bin/pip3 install esptool
ln -s ~/Library/Python/3.9/bin/esptool.py ~/Library/Arduino15/packages/esp32/tools/esptool_py/4.5.1/esptool.py
Note: Specify
/usr/bin/pip3to avoid installing in the Homebrew directory.
Reset ESP32
After writing completes, press and release the ESP32 reset switch EN(RST) on TWELITE SPOT to reset ESP32.

Reset Switch Position
3 - How to Upload Files to ESP32 (Arduino IDE 2.x)
data/ folder) to the ESP32 mounted on TWELITE SPOT.This section covers advanced topics (how to treat the flash area of the ESP32 mounted on TWELITE SPOT as a file system and upload files like HTML).
If you don’t have requirements such as uploading HTML files to TWELITE SPOT to make it function as a web server (achieved in the spot-server sample) or uploading encryption key files to TWELITE SPOT, you can ignore this section.
This section uses third-party open source software.
We cannot provide detailed usage instructions for third-party software. Also, we assume no responsibility for any damage caused by using third-party software.
Installing the Plugin
Install the Arduino IDE 2.x plugin (earlephilhower/arduino-littlefs-upload) for uploading files to the ESP32 flash area.
Download the Plugin
Download arduino-littlefs-upload-x.x.x.vsix from the following page:
Releases · earlephilhower/arduino-littlefs-upload
Install the Plugin
Place the downloaded arduino-littlefs-upload-x.x.x.vsix in .arduinoIDE/plugins under your user directory.
- Windows example:
C:\Users\foo\.arduinoIDE\plugins\ - macOS/Linux example:
~/.arduinoIDE/plugins/
Host Connection
Connect TWELITE R3 / R2
Connect TWELITE R3 / R2 to the 7P interface (the side marked ESP32).
Connect Power
Supply 5V power to the side USB-C connector.

Connection example (ESP32)
Arduino IDE Operations
Open Sketch
Launch Arduino IDE and open your sketch.
Place Files to Upload
Open the sketch folder from Sketch -> Show Sketch Folder.
Create a
datafolder at the same level as the sketch file (.ino).Place the files you want to upload inside the
datafolder.
data folder is preserved in the flash area.Select Serial Port
Select the TWELITE R3 / R2 port from Tools -> Port menu.
COM? on Windows, and /dev/tty? on macOS / Linux.Start ESP32 in Program Mode
Press the ESP32 reset switch EN(RST) and ESP32 boot switch BOOT on TWELITE SPOT, then release them in the order EN(RST) -> BOOT.

Button locations
BOOT while resetting, you can put the ESP32 into program mode.Execute Upload
Press
Ctrl+Shift+P(or⌘+Shift+Pon macOS) to open the command palette.Select
Upload LittleFS to Pico/ESP8266/ESP32.
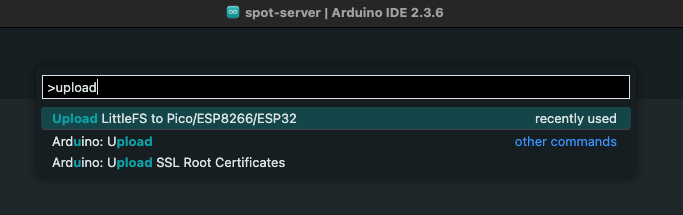
Command palette screen
Completed upload. will be displayed at the bottom of the screen.Reset ESP32
After the upload is complete, press and release the ESP32 reset switch EN(RST) on TWELITE SPOT to reset the ESP32.

Reset switch location
4 - How to Specify the Partition Table for Writing to ESP32
This article introduces an advanced topic (how to specify the partition table of the flash area).
If you use the partition table settings included by default in the ESP32 Arduino Core (e.g., Default 4MB with spiffs), you can ignore this article.
Creating the Definition File
The partition table is defined in a csv file.
In the example below, out of the 16MB flash area, 8MB is allocated for the file system.
# TWELITE SPOT 16MB with 8MB LittleFS
# Name, Type, SubType, Offset, Size, Flags
nvs, data, nvs, 0x9000, 0x5000,
otadata, data, ota, 0xE000, 0x2000,
app0, app, ota_0, 0x10000, 0x7F0000,
spiffs, data, spiffs, 0x800000, 0x800000,
TWELITE SPOT 16MB with 8MB LittleFSis the name displayed in the Arduino IDE.nvsis the area used by the system. Do not change.otadatais the area used when using OTA. Do not change.app0is the area where the firmware is written.spiffsis the area used by the LittleFS file system.
The units of the Offset and Size columns in the csv file are bytes, expressed in hexadecimal.
Therefore, the usable sizes for firmware and file system in the above example can be calculated as follows:
- Size of
app0:0x7F0000 = 8323072, approximately7.875MB - Size of
spiffs:0x800000 = 8388608, exactly8MB
Registering the Definition File
Open the Arduino15 folder and add the csv file to the following path:
Arduino15/packages/esp32/hardware/esp32/x.x.x/tools/partitions
x.x.xis the version of Arduino core for the ESP32
Applying the Partition Table
From the Arduino IDE toolbar, open Tools -> Partition Scheme and select the added partition table.
The selected partition table will be applied to subsequent firmware and file system writes.
partitions.csv is placed in the same location as the sketch file, that file takes precedence. However, the display in the Arduino IDE does not change, which may cause confusion.