Remote Control App Operating Modes
List of Operating Modes
Each mode is set by connecting the Mx pins to either not connected (OPEN) or to GND.
M3 | M2 | M1 | Mode | Function | Power | Initial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | O | O | Child: | Sends input states to the parent device and always waits for received data to reflect it on output | 120 | |
| O | O | G | Parent: | Sends input states to child devices and always waits for received data to reflect it on output | 0 | |
| O | G | O | Repeater: | Always waits for received data and relays it | 122 | |
| O | G | G | Child: | Sends input states to the parent device frequently and always waits for received data to reflect it on output | 123 | |
| G | O | O | Child: | Sends input states to the parent device every second, disables reception, and always enters power saving mode | ✅ | 124 |
| G | G | O | (Pairing Mode) | Details | ||
| G | G | G | Child: | Sends input states to the parent device every 10 seconds, disables reception, and always enters power saving mode | ✅ | 127 |
O: Not connected (OPEN), G: Connected to
GND
Initial mode is Child: Continuous mode.
The initial Logical Device ID (LID) used to identify the device differs depending on the mode.
Only in parent or repeater modes, you can switch the LID in Interactive Mode.
Please set parent to 121 and repeater to 122.
Parent Device
Continuous Mode
Parent: Continuous Mode
When a change in signal input is detected, or every second, data is sent to all child devices.
It also always waits for data sent from child devices, so it responds quickly but continuously consumes power.
- Reception: Always waiting
- Transmission: On input change / every 1 second
Child Device
Continuous Mode
Child: Continuous Mode
When a change in signal input is detected, or every second, data is sent to all parent devices.
It also always waits for data sent from parent devices, so it responds quickly but continuously consumes power.
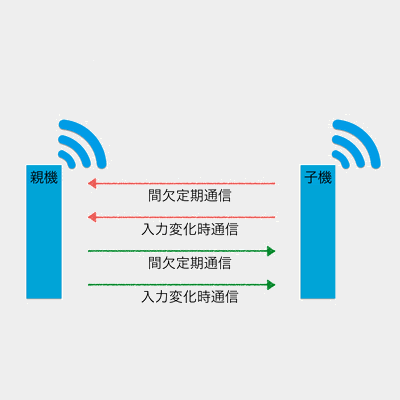
Image of communication with parent device
- Reception: Always waiting
- Transmission: On input change / every 1 second
Disable periodic transmission
0x00000020 in Interactive Mode.Child: Continuous 0.03s Mode
This mode shortens the periodic transmission interval of Child: Continuous Mode from 1 second to 0.03 seconds.
Although it always waits for data sent from the parent device, it occupies the bandwidth of communication from child to parent, causing slower response to parent input. It continuously consumes power.

Image of communication with parent device
- Reception: Always waiting
- Transmission: On input change / every 0.03 seconds
Intermittent Mode
Child: Intermittent 1s Mode
When a change in signal input is detected, or every second, the power saving mode is disabled and data is sent to all parent devices.
Reception is disabled, so it cannot be controlled by the parent device. This mode has excellent power saving performance.
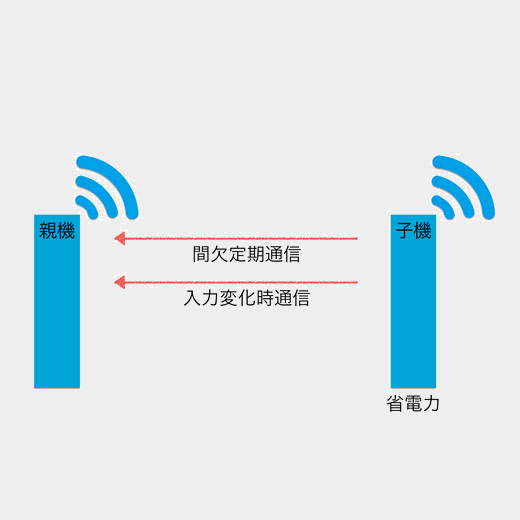
Image of communication with parent device
- Reception: Disabled
- Transmission: On input change / every 1 second
Child: Intermittent 10s Mode
When a change in signal input is detected, or every 10 seconds, the power saving mode is disabled and data is sent to all parent devices.
Reception is disabled, so it cannot be controlled by the parent device. This mode has excellent power saving performance.

Image of communication with parent device
- Reception: Disabled
- Transmission: On input change / every 10 seconds
Repeater Device
Continuous Mode
Repeater: Continuous Mode
The repeater transmits received packets.
You can install up to three repeaters between parent and child devices, but increasing repeaters increases the number of packets, which can cause interference.
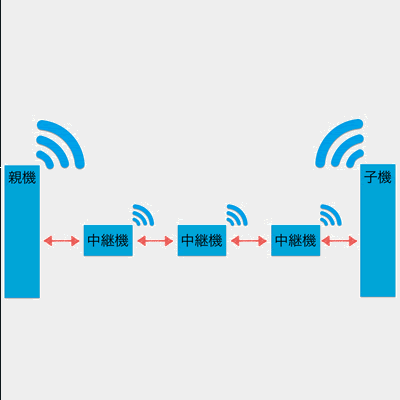
Image of relay
- Reception: Always waiting
- Transmission: On reception