Repeater Mode of Parent and Repeater App
Example Settings
To use as a repeater, set the Operating Mode in interactive mode to 1 or higher.
Relay Methods
TWELITE NET provides two major relay methods for wireless packet delivery, as shown in the table below, which differ depending on the application. This app can identify and relay packets of the applications shown in the table below.
| Relay Method | Supported Applications |
|---|---|
| Simple Net | Extremely Simple! Standard App, Remote Control App, Serial Communication App, ACT |
| Relay Net | Wireless Tag App, PAL App, CUE App |
Relay Using Simple Net
When relaying applications using Simple Net, setting the operating mode to 1 or higher allows up to three relays.
For example, in case 1., if there are up to 3 Repeaters between the Parent and Child, data will reach the Parent, but in case 2., if there are 4 or more Repeaters, data will not reach the Parent.
1. Child ---> Repeater ---> Repeater ---> Repeater ---> Parent
→ Parent can receive Child's data relayed 3 times.
2. Child ---> Repeater ---> Repeater ---> Repeater ---> Repeater -x-> Parent
→ Stops relaying at the 4th relay.
Relaying with Simple Net basically uses broadcast communication and relays all received packets. The advantage is that communication to form and maintain the relay network is not necessary, but the disadvantage is that communication volume can explode as the number of Repeaters increases.
For details, please refer to here.
Relay Using Relay Net
For relaying data of applications using Relay Net with one stage of relay, set the operating mode value to 1.
When performing multiple relays, increase the operating mode setting value as the distance from the Parent increases. (It is acceptable if the setting values are in ascending order even if some values are skipped.)
The maximum number of relays for this method is up to 63 times.
Example 1: One relay\
Child ---> Repeater (Operating Mode: 1) ---> Parent
Example 2: Two relays\
Child ---> Repeater (Operating Mode: 2) ---> Repeater (Operating Mode: **1**) ---> Parent
Example 3: Three relays\
Child ---> Repeater (Operating Mode: 6) ---> Repeater (Operating Mode: 3) ---> Repeater (Operating Mode: 1) ---> Parent
Relay Net is a tree-type network designed to efficiently deliver upstream packets. Repeaters search for an upper layer (Parent or Repeater with a smaller operating mode setting) and relay to one discovered upper layer device.
Therefore, even if the number of Repeaters increases, the communication volume is less likely to become large compared to Simple Net, but communication occurs to discover and maintain the connection destination.
For details, please see here.
When Performing Static Routing (Directly Specifying Relay Destination)
When relaying with Relay Net, considering the layout as shown in the figure below, Repeater 2 automatically selects either the Parent or Repeater 1 as the connection destination.
Basically, fewer relays tend to have a higher delivery rate to the Parent, but if the Parent is selected as the connection destination for Repeater 2, communication quality may deteriorate due to obstacles between Parent and Repeater 2, resulting in a lower delivery rate to the Parent than when relaying through Repeater 1.
Therefore, this app has a function (static routing function) to specify the connection destination of Repeaters by TWELITE serial number.
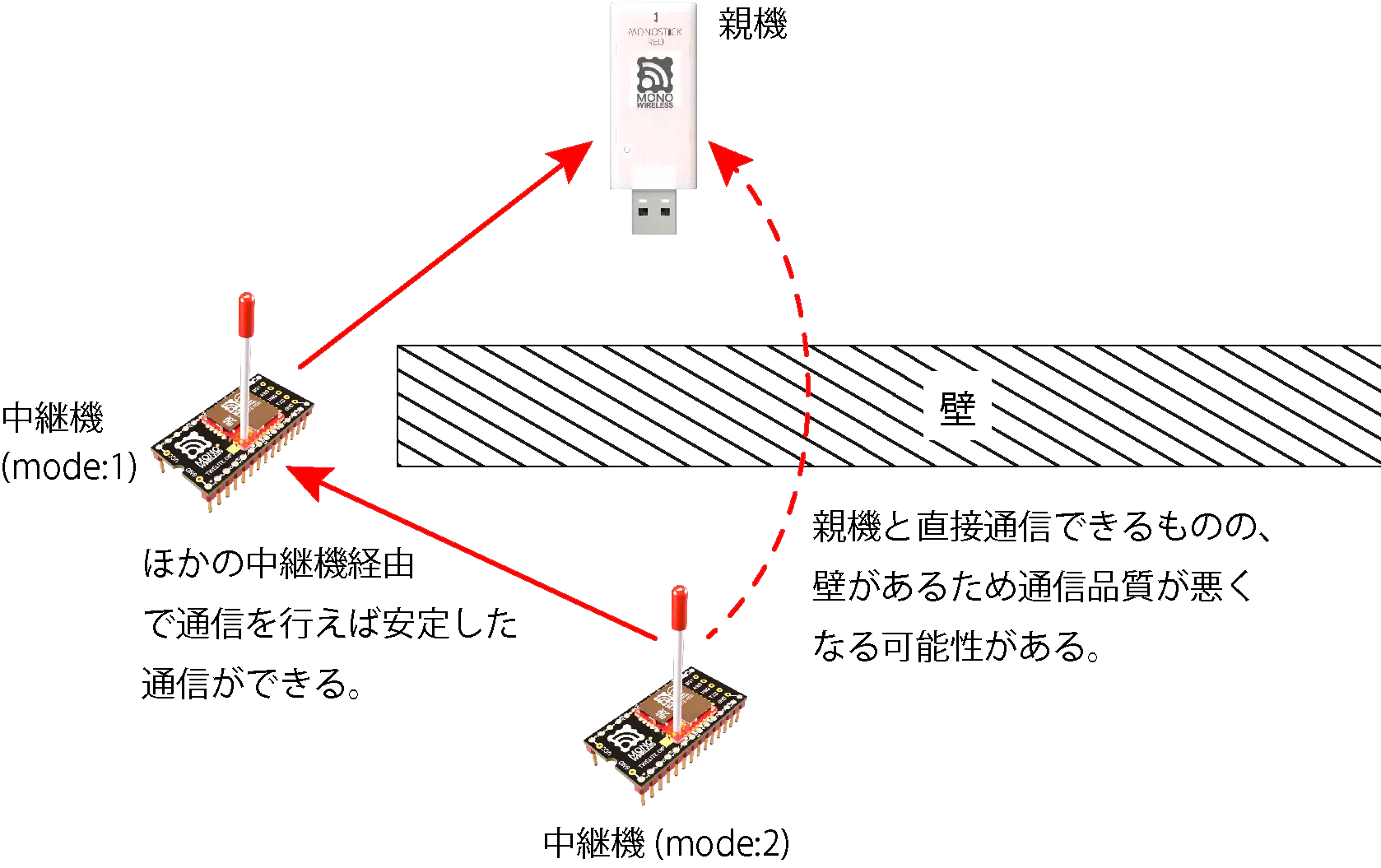
When performing static routing, set the route from Repeater 2 to Repeater 1 statically, or set all routes statically.
Setting all routes increases the amount of configuration and does not support redundancy for situations such as Repeater failure or changes in radio conditions, but it eliminates the time to determine the upper communication destination and allows prompt relay operation.
To perform static routing, set the connection destination as shown in the table below: Repeater 1’s connection destination is the Parent’s SID, and Repeater 2’s connection destination is Repeater 1’s SID.
Example: Two-stage relay (Parent ← Repeater 1 ← Repeater 2 ← Child)
| TWELITE SID Example | Connection Destination (A: Access Point Address) Setting Example | Operating Mode (l:Mode) Setting Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parent | 810F155E | - | 0 |
| Repeater 1 | 810E18E8 | 810F155E (Parent’s SID)※ | 1 |
| Repeater 2 | 810F17FF | 810E18E8 (Repeater 1’s SID) | 2 |
※ If you only want to deal with effects caused by walls as shown in the figure, this setting is unnecessary.