Communicating with Child Devices Using Python (Graphical UI)
Communicating with TWELITE DIP
Let’s build an application to communicate with the TWELITE DIP, featuring a simple user interface.
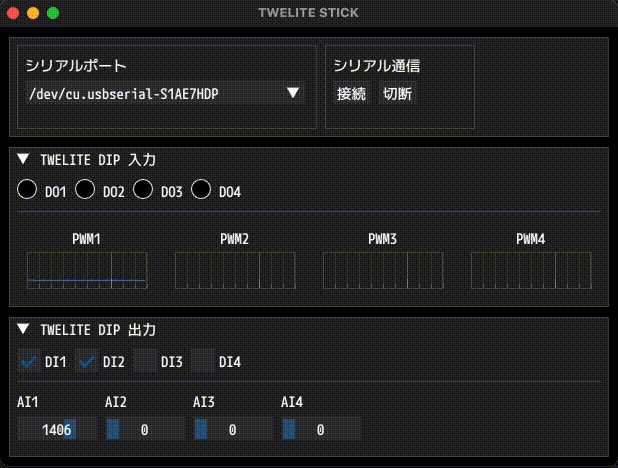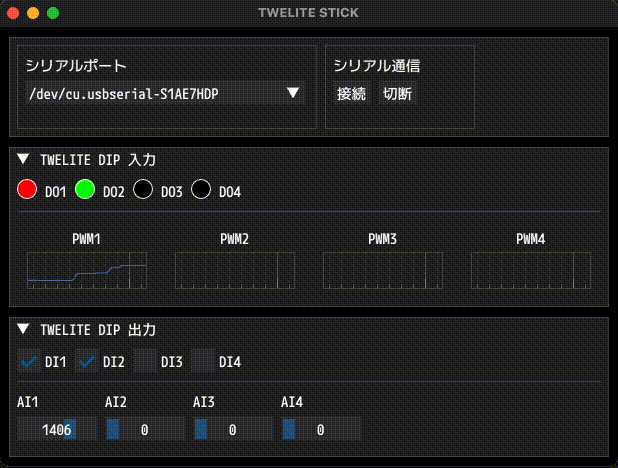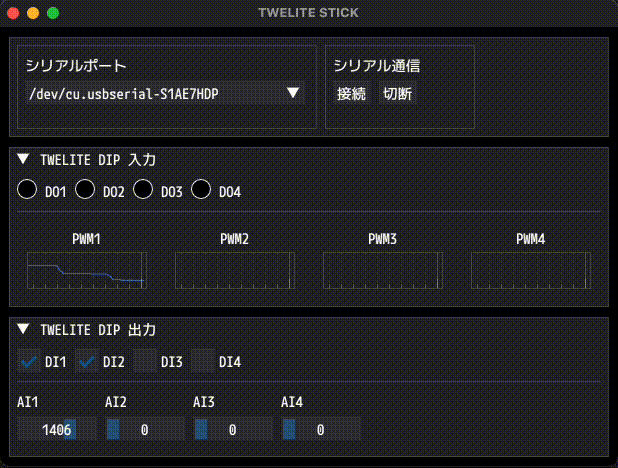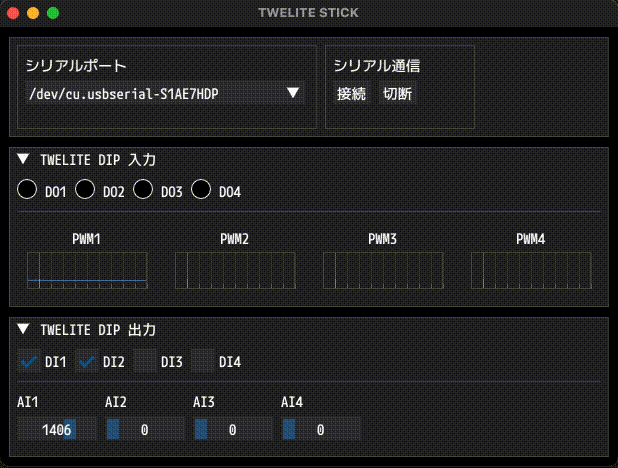
Example of screen display
In the basic script for TWELITE DIP, we only performed simple operations with DI1 and DO1. However, applications designed for actual monitoring require a user interface like the one found in TWELITE STAGE APP.
About Dear PyGui
Here, we will use a combination of Dear PyGui and the MWings library.
Dear PyGui (DPG) is a UI toolkit based on Dear ImGui written in C++ and OpenGL.
It is commonly used in development tool interfaces. While it is not suited for highly customized designs, it features lightweight performance and simple syntax.
Wiring and Starting the TWELITE DIP
In this application, when a signal is received via DIx or AIx of the TWELITE DIP, a signal is simultaneously output to DOx or PWMx.
In addition to VCC and GND, freely connect any of the following 16 pins:
| Type | Pin | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Input | DIx | #15 | #16 | #17 | #18 | 0.0V - VCC | Internal pull-up |
| Analog Input | AIx | #22 | #23 | #24 | #25 | 0.0V - 2.0V | Invalid if exceeded |
| Digital Output | DOx | #5 | #8 | #9 | #12 | 0.0V - VCC | Connect LED cathode |
| PWM Output | PWMx | #4 | #6 | #7 | #11 | 0% - 100% | Voltage at VCC level |
Creating and Running the Script
Installing Modules
Install the mwings (or mwingslite) and dearpygui modules.
pip install mwings dearpygui
Creating the Script
Create the script stick_dip_gui.py as described below. It uses mwings.parsers.app_twelite to receive data and mwings.serializers.app_twelite to send data, with a GUI provided via dearpygui.
A font file can be used to display components.
In this example, it is assumed that Mplus1Code-Medium.otf from M PLUS FONTS is located in the same directory.
Project
├ stick_dip_gui.py
└ Mplus1Code-Medium.otf
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from time import perf_counter
from enum import IntEnum, auto
from zoneinfo import ZoneInfo
from typing import Any, Self, final
from types import TracebackType
from pathlib import Path
from collections import deque
import mwings as mw
import dearpygui.dearpygui as dpg # type: ignore
PLOT_UPDATE_INTERVAL = 1.0 / 100 # 100Hz
PLOT_X_LIMIT = 5.0 # 3 seconds
FONT = "Mplus1Code-Medium.otf"
# MARK: MainViewport
@final
class MainViewport:
@final
class State(IntEnum):
"""Application state enumeration."""
IDLE = auto()
CONNECTING = auto()
selected_port: str
twelite: mw.Twelite
command_app_twelite: mw.serializers.app_twelite.Command
pwm_data: dict[int, int]
pwm_plot_data: dict[int, deque[tuple[float, int]]]
last_plot: float
state: State
theme_disabled: int
def __init__(self) -> None:
"""Initialize the main window and prepare all components."""
self.initialize_viewport()
self.create_themes()
self.create_windows()
self.initialize()
self.update_state(self.State.IDLE)
def create_themes(self) -> None:
"""Create a visual theme for disabled UI elements."""
with dpg.theme() as self.theme_disabled:
with dpg.theme_component(dpg.mvAll):
dpg.add_theme_color(dpg.mvThemeCol_Text, (150, 150, 150, 255))
dpg.add_theme_color(dpg.mvThemeCol_TextDisabled, (100, 100, 100, 255))
dpg.add_theme_color(dpg.mvThemeCol_FrameBg, (5, 5, 5, 255))
# MARK: Initialize Viewport
def initialize_viewport(self) -> None:
"""Set up Dear PyGui context, fonts, and viewport."""
dpg.create_context()
with dpg.font_registry():
font_path = str(Path(__file__).parent / FONT)
with dpg.font(file=font_path, size=18) as default_font:
dpg.add_font_range_hint(dpg.mvFontRangeHint_Japanese)
dpg.bind_font(default_font)
dpg.create_viewport(
title="TWELITE STICK", width=620, height=440, resizable=True
)
dpg.set_viewport_vsync(False)
dpg.setup_dearpygui()
dpg.show_viewport()
def create_windows(self) -> None:
"""Create and configure all Dear PyGui windows and their contents."""
# MARK: Panel Window
with dpg.window(
no_title_bar=True,
no_close=True,
no_collapse=True,
no_move=True,
no_resize=True,
pos=(10, 10),
width=600,
height=100,
):
ports = mw.utils.get_ports()
with dpg.group(horizontal=True):
with dpg.child_window(width=300):
dpg.add_text("Serial Port")
dpg.add_combo(
items=ports,
default_value=ports[0],
tag="ports_combo",
width=280,
enabled=True,
callback=self.on_select_port,
)
with dpg.child_window(width=150):
dpg.add_text("Transmission")
with dpg.group(horizontal=True):
dpg.add_button(
label="Connect",
tag="start_button",
enabled=True,
callback=self.on_start,
)
dpg.add_button(
label="Disconnect",
tag="stop_button",
enabled=False,
callback=self.on_stop,
)
# MARK: Input Window
with dpg.window(
label="TWELITE DIP Input",
no_close=True,
# no_resize=True,
pos=(10, 120),
width=600,
height=160,
tag="window_twelite_dip_input",
):
with dpg.group(horizontal=False):
# DOx
with dpg.group(horizontal=True):
for p in range(1, 5):
with dpg.group(horizontal=True):
with dpg.drawlist(
width=20, height=20, tag=f"indicator_do{p}"
):
dpg.draw_circle(
center=(10, 10),
radius=10,
fill=(0, 0, 0, 255),
tag=f"circle_do{p}",
)
dpg.add_text(f"DO{p}")
dpg.add_spacer()
dpg.add_separator()
dpg.add_spacer()
# PWMx
with dpg.group(horizontal=True):
for p in range(1, 5):
with dpg.plot(
label=f"PWM{p}",
height=80,
width=140,
tag=f"plot_pwm{p}",
no_frame=True,
no_mouse_pos=True,
):
dpg.add_plot_axis(
dpg.mvXAxis,
tag=f"plot_pwm{p}_x",
no_tick_labels=True,
)
with dpg.plot_axis(
dpg.mvYAxis,
tag=f"plot_pwm{p}_y",
no_tick_labels=True,
no_tick_marks=True,
no_gridlines=True,
):
dpg.add_line_series(
[],
[],
tag=f"series_pwm{p}",
parent=f"plot_pwm{p}_y",
)
# MARK: Output Window
with dpg.window(
label="TWELITE DIP Output",
no_close=True,
no_resize=True,
pos=(10, 290),
width=600,
height=140,
tag="window_twelite_dip_output",
):
with dpg.group(horizontal=False):
# DIx
with dpg.group(horizontal=True):
for p in range(1, 5):
dpg.add_checkbox(
label=f"DI{p}",
tag=f"checkbox_di{p}",
enabled=False,
callback=self.on_check_di,
user_data=p,
)
dpg.add_spacer()
dpg.add_separator()
dpg.add_spacer()
# AIx
with dpg.group(horizontal=False):
with dpg.group(horizontal=True):
for p in range(1, 5):
with dpg.group(horizontal=False):
dpg.add_text(f"AI{p}")
dpg.add_slider_int(
label="",
width=80,
default_value=0,
min_value=0,
max_value=2000,
tag=f"slider_ai{p}",
enabled=False,
callback=self.on_change_ai,
user_data=p,
)
def update_state(self, new_state: State) -> None:
"""Update the UI and internal state based on the application's current status."""
# MARK: UI State
self.state = new_state
match new_state:
case self.State.IDLE:
dpg.configure_item("ports_combo", enabled=True)
dpg.configure_item("start_button", enabled=True)
dpg.configure_item("stop_button", enabled=False)
for p in range(1, 5):
dpg.configure_item(f"checkbox_di{p}", enabled=False)
dpg.configure_item(f"slider_ai{p}", enabled=False)
dpg.bind_item_theme("window_twelite_dip_input", self.theme_disabled)
dpg.bind_item_theme("window_twelite_dip_output", self.theme_disabled)
case self.State.CONNECTING:
dpg.configure_item("ports_combo", enabled=False)
dpg.configure_item("start_button", enabled=False)
dpg.configure_item("stop_button", enabled=True)
for p in range(1, 5):
dpg.configure_item(f"checkbox_di{p}", enabled=True)
dpg.configure_item(f"slider_ai{p}", enabled=False)
dpg.bind_item_theme("window_twelite_dip_input", 0)
dpg.bind_item_theme("window_twelite_dip_output", 0)
# MARK: UI Handlers
def on_select_port(self, sender: Any, app_data: str, user_data: Any) -> None:
"""Handle serial port selection from the combo box."""
self.selected_port = app_data
def on_start(self, sender: Any, app_data: str, user_data: Any) -> None:
"""Handle the start button click and initiate communication."""
self.start()
def on_stop(self, sender: Any, app_data: str, user_data: Any) -> None:
"""Handle the stop button click and terminate communication."""
self.update_state(self.State.IDLE)
self.twelite.close()
def on_check_di(self, sender: Any, app_data: bool, user_data: int) -> None:
"""Handle checkbox state changes for DI output control."""
if 1 <= user_data <= 4:
self.command_app_twelite.di_state[user_data - 1] = app_data
self.twelite.send(self.command_app_twelite)
def on_change_ai(self, sender: Any, app_data: int, user_data: int) -> None:
"""Handle slider changes for AI values and send PWM updates."""
if 1 <= user_data <= 4:
self.command_app_twelite.pwm_duty[user_data - 1] = app_data * 1024 // 2000
self.twelite.send(self.command_app_twelite)
# MARK: Packet handler
def on_app_twelite(self, packet: mw.parsers.app_twelite.ParsedPacket) -> None:
"""Update the GUI based on incoming TWELITE DIP packet data."""
now = perf_counter()
for p in range(1, 5):
# DO
p_state = packet.di_state[p - 1]
match p:
case 1: # RED
color = (255, 0, 0, 255) if p_state else (0, 0, 0, 255)
case 2: # GREEN
color = (0, 255, 0, 255) if p_state else (0, 0, 0, 255)
case 3: # YELLOW
color = (255, 255, 0, 255) if p_state else (0, 0, 0, 255)
case 4: # BLUE
color = (0, 0, 255, 255) if p_state else (0, 0, 0, 255)
dpg.configure_item(f"circle_do{p}", fill=color)
# PWM
self.pwm_data[p] = packet.ai_voltage[p - 1]
self.pwm_plot_data[p].append((now, self.pwm_data[p]))
# MARK: Plot
def update_plot(self) -> None:
"""Update the plot with the latest PWM data."""
now = perf_counter()
# Throttle plot updates to PLOT_UPDATE_INTERVAL
if now - self.last_plot < PLOT_UPDATE_INTERVAL:
return
self.last_plot = now
for p in range(1, 5):
# If no new value was added recently, duplicate the last value
if self.pwm_plot_data[p]:
last_time, last_val = self.pwm_plot_data[p][-1]
if now - last_time > PLOT_UPDATE_INTERVAL:
self.pwm_plot_data[p].append((now, last_val))
else:
self.pwm_plot_data[p].append((now, self.pwm_data[p]))
# Remove old values older than PLOT_X_LIMIT
while (
self.pwm_plot_data[p]
and now - self.pwm_plot_data[p][0][0] > PLOT_X_LIMIT
):
self.pwm_plot_data[p].popleft()
x_series, y_series = (
zip(*list(self.pwm_plot_data[p])) if self.pwm_plot_data[p] else ([], [])
)
if x_series and y_series:
dpg.set_value(f"series_pwm{p}", [x_series, y_series])
dpg.set_axis_limits(f"plot_pwm{p}_x", x_series[0], x_series[-1])
dpg.set_axis_limits(f"plot_pwm{p}_y", 0, 2000)
# MARK: Initialize Variables
def initialize(self) -> None:
"""Initialize internal command structure and default values."""
ports = mw.utils.get_ports()
self.selected_port = ports[0] # default
command_app_twelite_initial: dict[str, Any] = {
"destination_logical_id": 0x78, # All child devices
"di_to_change": [True, True, True, True], # Enable DI1-4
"di_state": [False, False, False, False], # Initial state of DIx
"pwm_to_change": [True, True, True, True], # Enable AI1-4
"pwm_duty": [0, 0, 0, 0], # Initial state of AIx
}
self.command_app_twelite = mw.serializers.app_twelite.Command(
**command_app_twelite_initial
)
self.pwm_data = {1: 0, 2: 0, 3: 0, 4: 0}
self.pwm_plot_data = {1: deque(), 2: deque(), 3: deque(), 4: deque()}
self.last_plot = 0.0
# MARK: Start
def start(self) -> None:
"""Start TWELITE communication and register listeners."""
# Create a twelite object
self.twelite = mw.Twelite(self.selected_port)
# Use JST for received data
self.twelite.set_timezone(ZoneInfo("Asia/Tokyo"))
# Register event handler(s)
self.twelite.add_listener(mw.common.PacketType.APP_TWELITE, self.on_app_twelite)
self.update_state(self.State.CONNECTING)
# MARK: loop
def loop(self) -> None:
"""Perform periodic updates while the application is running."""
match self.state:
case self.State.IDLE:
pass
case self.State.CONNECTING:
self.twelite.update()
self.update_plot()
dpg.render_dearpygui_frame()
# MARK: Show
def show(self) -> None:
"""Main execution loop of the application."""
try:
while dpg.is_dearpygui_running():
self.loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
finally:
print("Quit...")
self.close()
# MARK: Lifecycle
def __enter__(self) -> Self:
"""Enter the runtime context related to this object."""
return self
def __exit__(
self,
exc_type: type[BaseException] | None,
exc_value: BaseException | None,
traceback: TracebackType | None,
) -> bool | None:
"""Exit the runtime context and close the connection."""
self.close()
return None
def __del__(self) -> None:
"""Destructor to ensure resources are cleaned up."""
self.close()
def close(self) -> None:
"""Cleanly shut down TWELITE connection and Dear PyGui context."""
if self.state == self.State.CONNECTING:
self.twelite.close()
dpg.destroy_context()
# MARK: Entry point
if __name__ == "__main__":
with MainViewport() as viewport:
viewport.show()
Running the Script
Run the script.
python stick_dip_gui.py
- Select the serial port (e.g.,
COM3,/dev/tty.usb*) from the combo box labeled “Serial Port” - Click the “Connect” button under “Transmission” to start communication
- Change the inputs of the TWELITE DIP and observe changes in the “TWELITE DIP Input” window
- Adjust the checkboxes and sliders in the “TWELITE DIP Output” window to modify outputs of the TWELITE DIP
- Click the “Disconnect” button to stop communication
- Close the window

Example of screen display
If the communication is successful, the state of the TWELITE DIP will be displayed in real time, and its outputs can be modified at any time.
Graph update timing
The real-time PWMx graph reflects the last 5 seconds of data at 10 ms intervals, determined by the variables at the top of the script:
PLOT_UPDATE_INTERVAL = 1.0 / 100 # 100Hz
PLOT_X_LIMIT = 5.0 # 3 seconds
Script Overview
The initialization of Dear PyGui is handled by initialize_viewport().
This function sets up the font file and defines the size of the OS window (referred to as the Viewport).
def initialize_viewport(self) -> None:
"""Set up Dear PyGui context, fonts, and viewport."""
...
The interface within the OS window is defined in create_windows().
Child windows on the screen are created using dpg.window(), and components are defined within them.
By assigning a tag to a component, you can modify its values and attributes from the program (similar to the id= in HTML).
def create_windows(self) -> None:
"""Create and configure all Dear PyGui windows and their contents."""
...
Buttons, combo boxes, sliders, and checkboxes that accept user input can register a callback.
def on_select_port(self, sender: Any, app_data: str, user_data: Any) -> None:
"""Handle serial port selection from the combo box."""
...
As with other scripts, data received from a child TWELITE is handled by an event handler.
When building an executable with Nuitka
When building an executable (e.g., .exe) using Nuitka, converting method bindings into C may cause self to be duplicated, resulting in too many arguments. In such cases, implement the callback by returning a closure as shown below.
from typing import Any, Callable
...
def cb_for_select_port(self) -> Callable[[Any, str, Any], None]:
"""Make a callback for serial port selection from the combo box."""
def callback(sender: Any, app_data: str, user_data: Any) -> None:
self.selected_port = app_data
return callback
...
dpg.add_combo(
...
callback=self.cb_for_select_port(),
)
In on_app_twelite(), data to be reflected in DOx is registered immediately using tag, and data for PWMx is passed to update_plot() via member variables.
def on_app_twelite(self, packet: mw.parsers.app_twelite.ParsedPacket) -> None:
"""Update the GUI based on incoming TWELITE DIP packet data."""
...
When the “Connect” button is pressed, start() is called.
This function initializes mwings.Twelite and registers the receive handler.
add_listener method is used instead of the decorator @on used previously.
def start(self) -> None:
"""Start TWELITE communication and register listeners."""
...
Because Dear PyGui is built on a low-level API, the application controls frame rendering directly, allowing you to define your own rendering loop. While the OS window is open, loop() is repeatedly called.
Once connected to the serial port, loop() performs the following three tasks:
- Handles incoming data via
mwings.Twelite.update() - Updates the
PWMxgraph viaupdate_plot() - Draws and updates the UI with
dpg.render_dearpygui_frame()
mwings.Twelite.update() is used instead of mwings.Twelite.start(), which launches a separate thread.
def loop(self) -> None:
"""Perform periodic updates while the application is running."""
...
The entire application runs when show() is called.
def show(self) -> None:
"""Main execution loop of the application."""
...
The program exits the rendering loop either when dpg.is_dearpygui_running() becomes False after closing the window, or upon receiving a KeyboardInterrupt (Ctrl+C), and then cleans up mwings.Twelite and dearpygui.