Battery Operation and Buffer Capacitor
A buffer capacitor is used when operating TWELITE with a small-capacity battery
To achieve low power consumption as a wireless microcontroller module for connecting things, it is necessary to suppress the current consumption of each process, but it is also very important to shorten the startup time and processing time. Even if the current consumption is low, low power consumption cannot be achieved if the processing time is long.
The following are typical current consumptions when sending one packet of 30 bytes.
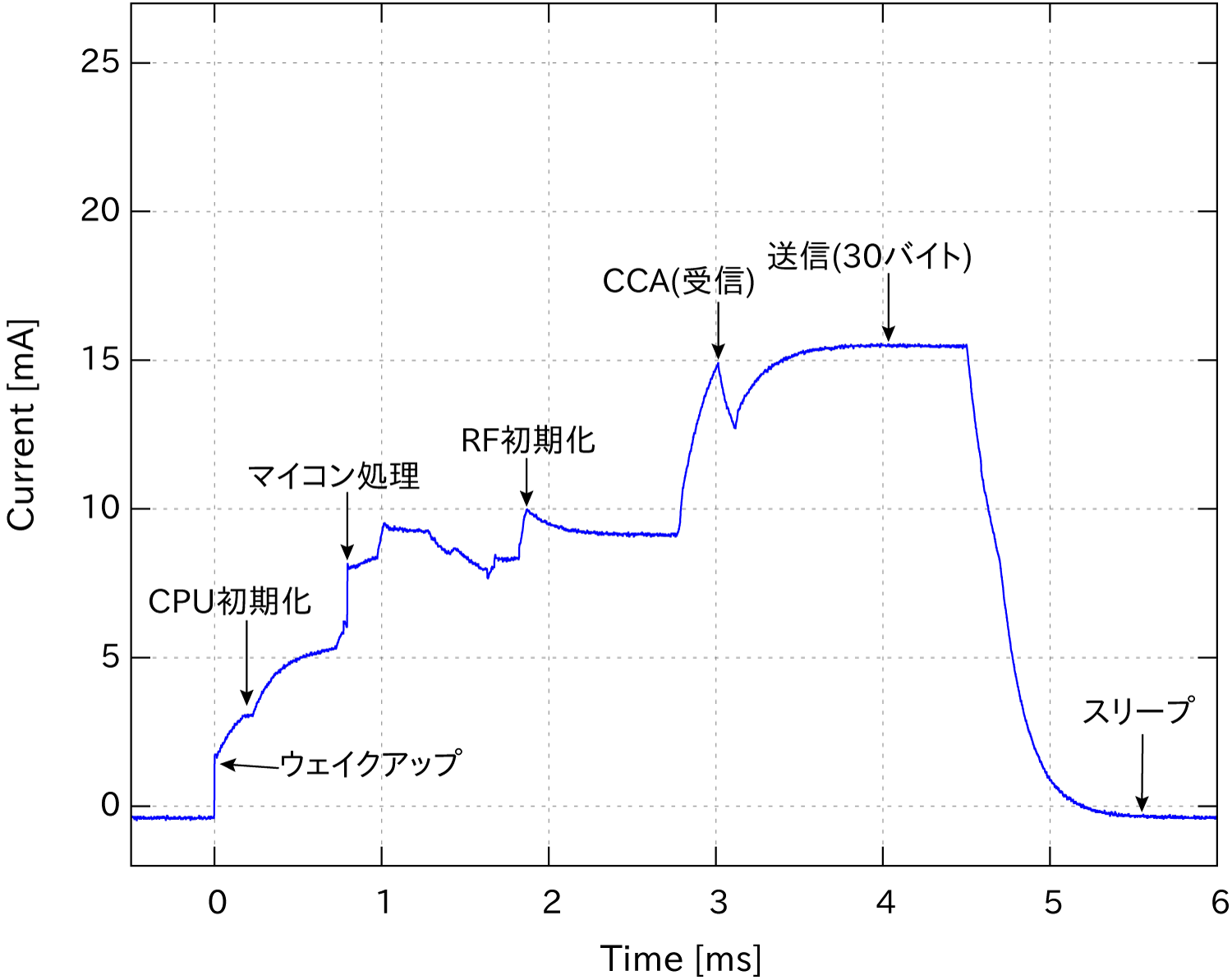
In the case of TWELITE BLUE
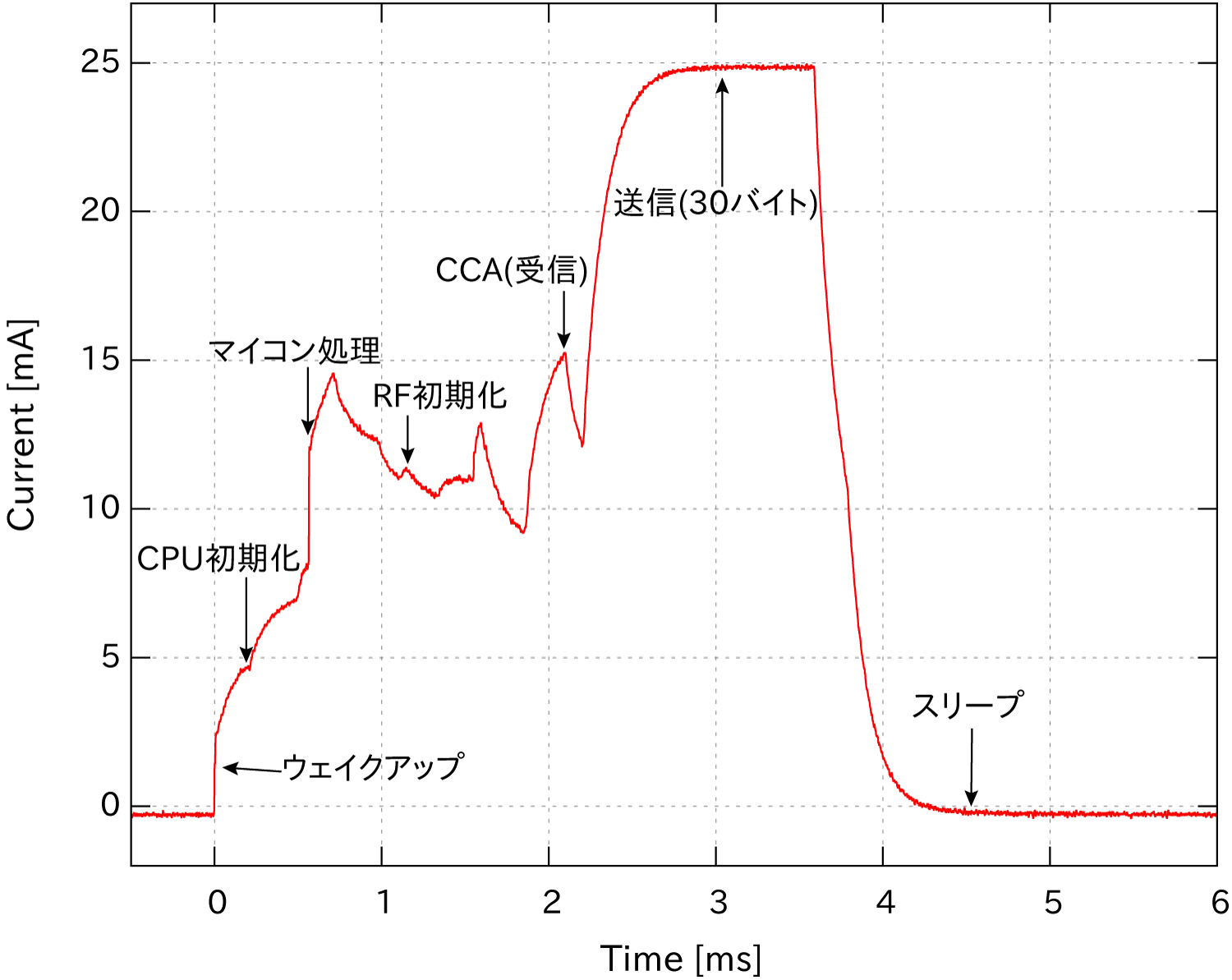
In the case of TWELITE RED
High output RED has a higher current consumption during transmission compared to standard output BLUE, but since the processing time is shorter, the current consumption for sending one packet is equivalent.
TWELITE achieves power saving through low current consumption, instant startup, and high-speed processing.
17.0mA and RED 14.7mA. If continuous reception is required, constant power supply or a battery with large capacity is necessary.Here is an example of a wireless tag with minimized power consumption of TWELITE. In this example, no sensors are used, and 4 bytes of ID data are periodically sent using the built-in timer. No reception acknowledgment (ACK) from the transmission counterpart is performed. The average current consumption when sending one packet is 11.6mA, and the processing time is 2.5ms.
11.6[mA] * (2.5/1000)[ms] = 29[uA]
29[uA] + 1.5[uA] = 30.5[uA] = 0.0305[mA]
Assuming transmission once every second and a CR2032 battery capacity of 220mAh,
220/( 0.0305 ) = approximately 7213[hours] = 300[days] = 10 months
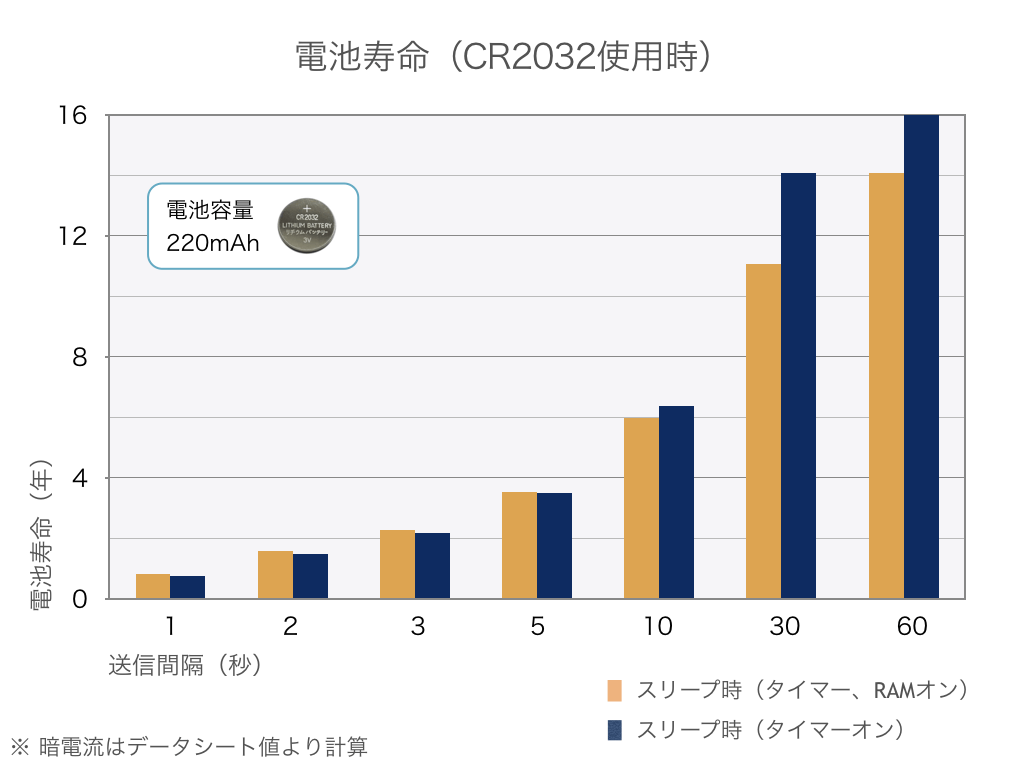
The graph below shows the battery life when using a coin-type battery (CR2032). The battery life exceeds 10 years when data is sent every 30 seconds.
A buffer capacitor is used when operating TWELITE with a small-capacity battery