This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print...
Software Development
1 - UART Communication Without the STAGE App
We assume no responsibility for the use of external tools.
Also, please refrain from asking questions regarding external tools.
When the TWELITE STAGE App is Not Suitable
The Terminal of the TWELITE STAGE app is intended only for simple evaluation purposes. Therefore, for advanced UART communication such as the serial communication app’s format modes (ASCII / Binary), there are the following issues:
- When inputting a sequence to TWELITE’s
RX, you must paste a pre-copied string usingAlt+V/⌘+V. - Binary data cannot be handled in HEX (hexadecimal) notation.
Overview of CoolTerm
CoolTerm is a general-purpose software specialized for serial communication. Unlike TeraTerm, it can handle binary data without using debug mode and supports multiple platforms.
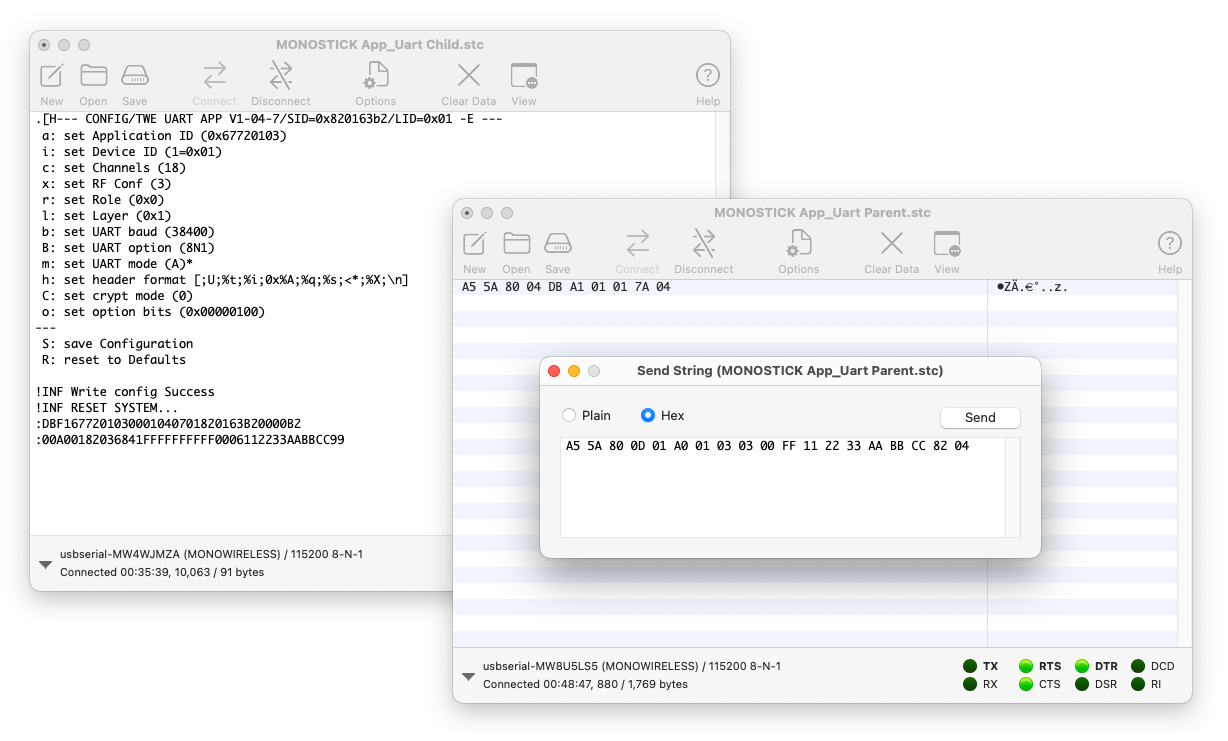
Using ASCII and Binary format modes of the serial communication app simultaneously
Installation
Please download the files from the author’s homepage.
Configuration
In CoolTerm, you can name the serial port and its associated settings.
Here, we introduce the necessary settings to adapt to the default TWELITE series.
Settings can be changed from the Options menu.
Serial Port
Within Options, under Serial Port, check the following settings:
Port: The port used by the TWELITE R or MONOSTICKBaudrate: Set to115200bps
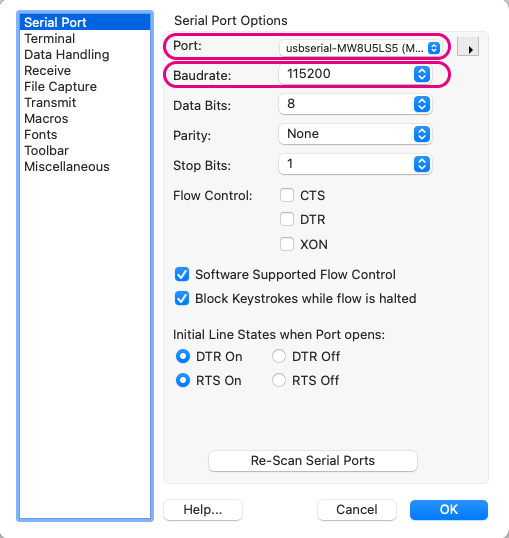
Example settings
Terminal
Within Options, under Terminal, mainly check the following settings:
Terminal Mode:Raw ModeEnter Key Emulation:CR+LF
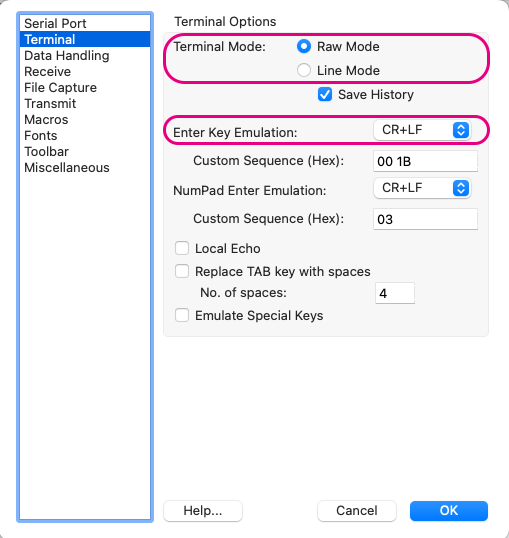
Example settings
When inputting ASCII data (excluding interactive mode), you may set Terminal Mode to Line Mode.
In Line Mode, pressing the Enter key sends the typed data at once.
Data Handling
Within Options, under Data Handling, mainly check the following settings:
Clear Display on: CheckESC[2J](enables screen clearing in interactive mode)- Check
Handle BS and DEL Characters(enables character deletion in interactive mode) Text Encoding:UTF8
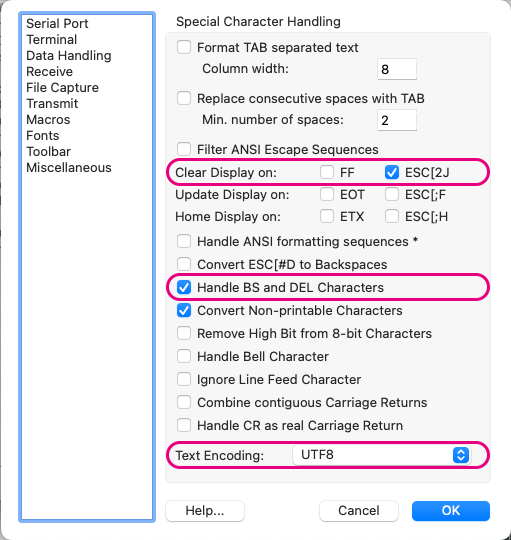
Example settings
Transmit
Within Options, under Transmit, mainly check the following settings:
Send String Options: CheckTerminate 'Send String' DataTermination String:0D 0A(appends CRLF at the end in the send screen)
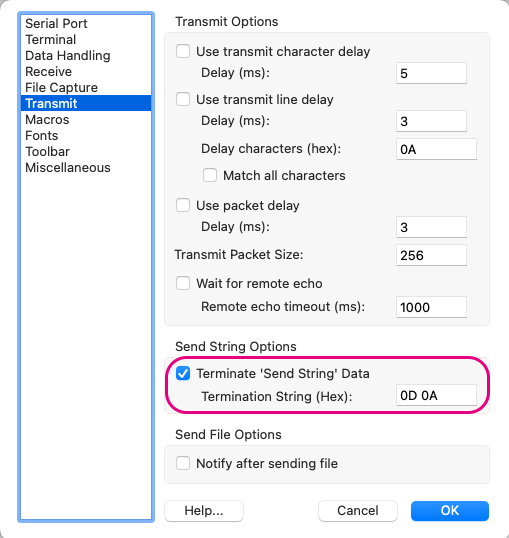
Example settings
Usage Examples
Interactive Mode
For interactive mode, it is recommended to set Options > Terminal > Terminal Mode to Raw Mode.
After clicking Connect, select the main screen and input the + character three times.
You can use interactive mode by directly typing characters just like in the TWELITE STAGE app.
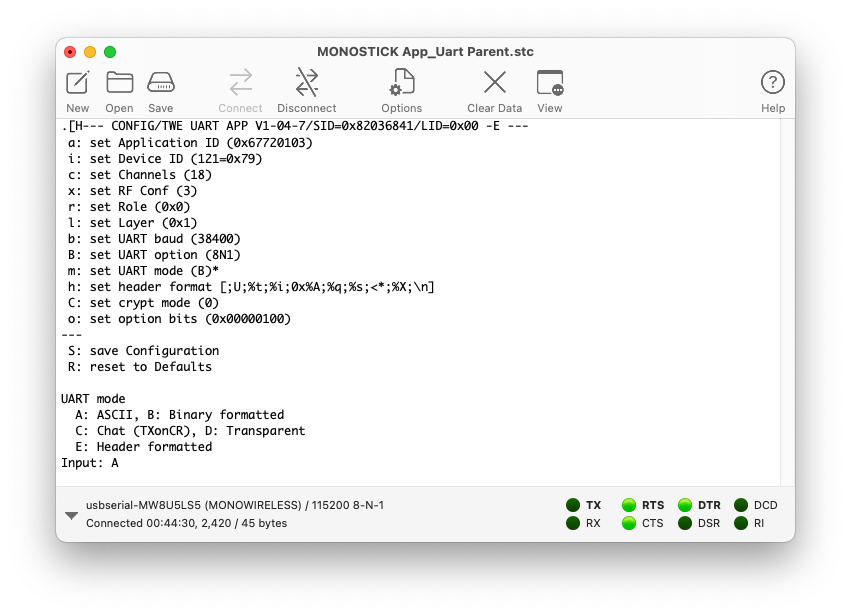
Example of using interactive mode
Serial Communication App Format Mode (ASCII)
When handling sequences composed of ASCII strings starting with : and ending with CRLF, as in the serial communication app’s ASCII format mode, setting Options > Terminal > Terminal Mode to Line Mode is convenient.
You can input line by line using the Enter key, and press the ↑ cursor key to refer to the history.
The following figure shows an example of sending the byte sequence 0x11 0x22 0x33 0xAA 0xBB 0xCC several times from the Parent to all Children using the simplified format.
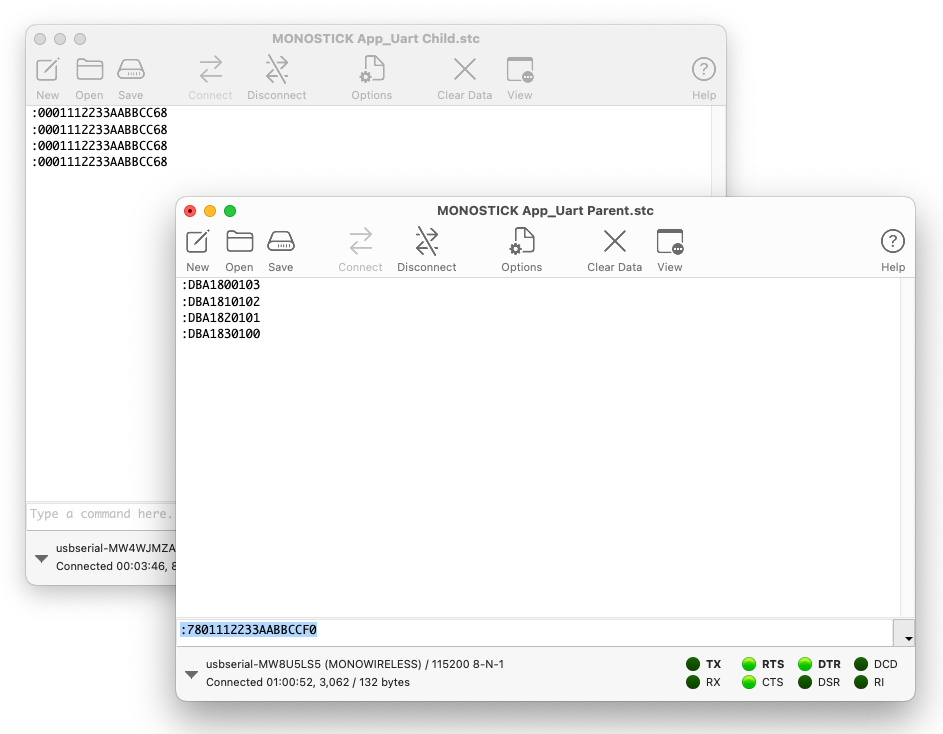
Example of using ASCII format mode
Serial Communication App Format Mode (Binary)
In the serial communication app’s binary format mode, set Options > Terminal > Terminal Mode to Raw Mode and uncheck Options > Transmit > Send String Options > Terminate 'Send String' Data.
To display received data in hexadecimal, select View > View Hex.
To send data represented in hexadecimal, select Connection > Send String... to open the send screen, and choose the Hex radio button.
The following figure shows an example of sending the byte sequence 0x11 0x22 0x33 0xAA 0xBB 0xCC from the Parent to all Children using the simplified format.
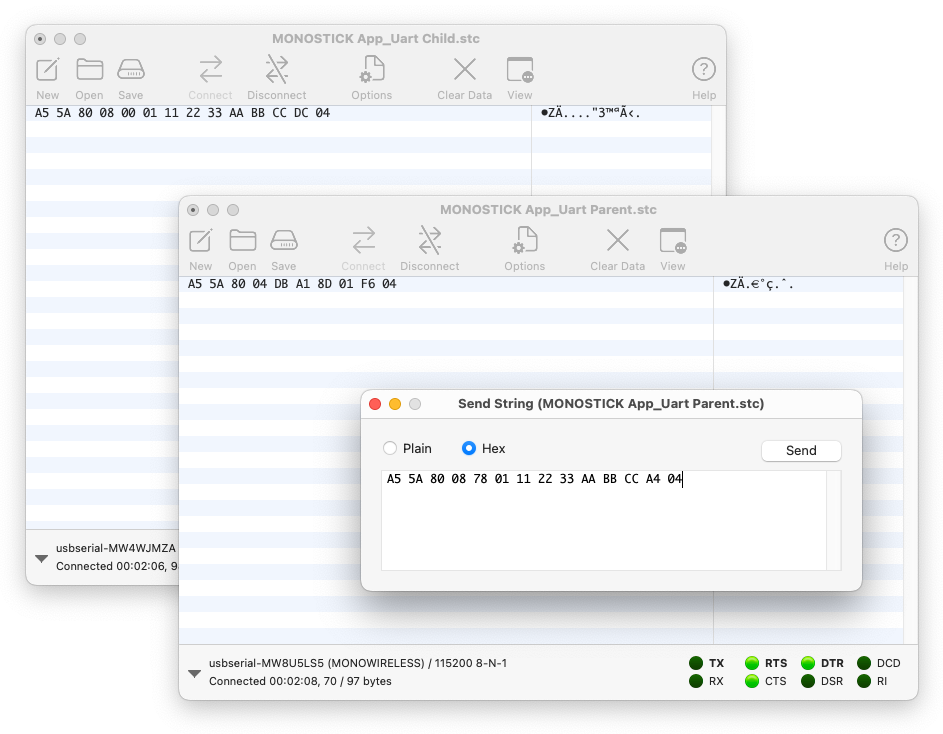
Example of using binary format mode
2 - Using Interactive Mode Programmatically
Since the interactive mode uses the serial port, it can also be operated programmatically.
In production processes, there may be situations where you want to use interactive mode automatically. Here, we introduce an example of reading and writing configuration values using Python.
Mechanism of Interactive Mode
In its initial state, the RX port of TWELITE operates at 115200bps 8N1. To transition into interactive mode, input + three times at intervals of approximately 200 to 1000ms, or for some applications, pull the SET pin low during startup. Since interactive mode accepts only ASCII characters as input, it can be freely controlled programmatically.
Implementation Example
Reading Configuration Values Using Python for Serial Communication App
Below is a script that reads the serial ID and configuration values from a TWELITE device programmed with the serial communication app App_Uart, via TWELITE R2/R3.
The tweliter module is used to identify TWELITE R2/R3, retrieve the serial port, and control the reset pin of TWELITE R2/R3.
pip install tweliter
Script
Using Python 3.12.
For the serial communication app specifications, we enter interactive mode by inputting + three times here.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import time
import re
from tweliter import Tweliter # Mono Wireless module for TWELITE R devices
def get_serial_id_and_settings() -> tuple[str, dict[str, str]] | None:
"""
Get the serial ID and settings from the interactive mode of a TWELITE R device.
Returns:
tuple[str, dict[str, str]] | None:
A tuple containing:
- str: the serial ID (e.g., "0x82010079")
- dict[str, str]: the settings dictionary (e.g., {'a': '0x67720103', ...})
Returns None if the device cannot be accessed or the output is invalid.
Notes:
Example output from the interactive mode of an App_Uart device:
--- CONFIG/TWE UART APP V1-04-6/SID=0x82010079/LID=0x78 -- ---
a: set Application ID (0x67720103)
i: set Device ID (120=0x78)
c: set Channels (18)
x: set RF Conf (3)
r: set Role (0x0)
l: set Layer (0x1)
b: set UART baud (38400)
B: set UART option (8N1)
m: set UART mode (E)
k: set Tx Trigger (sep=0x0d0a, min_bytes=0 dly=0[ms])
h: set header format [;U;%t;%i;0x%A;%q;%s;<*;%X;\n]
C: set crypt mode (0)
o: set option bits (0x00000100)
---
S: save Configuration
R: reset to Defaults
"""
try:
with Tweliter(
type_filter=Tweliter.Type.TWELITE_R2 | Tweliter.Type.TWELITE_R3
) as liter:
# Reset the device
liter.reset_device()
# Get the serial port instance (pyserial)
ser = liter.get_serial_instance()
ser.timeout = 1.0
# Enter to the interactive mode
for _ in range(3):
ser.write("+")
time.sleep(0.3)
# Read the output
raw_output = ser.read_until(b"S:").decode("utf-8")
# Reset the device (Exit interactive mode)
liter.reset_device()
except IOError as e:
print(f"Couldn't open the device {e}")
return None
# Find the settings block in the output
filter_output = re.search(r"---(.*?)---(.*?)---", raw_output, re.DOTALL)
if filter_output:
information_line = filter_output.group(1)
settings_block = filter_output.group(2)
else:
print("No settings block found.")
return None
# Extract serial id from the information line
serial_id_match = re.search(r"SID=0x([0-9A-Fa-f]+)", information_line)
if serial_id_match:
serial_id = f"0x{serial_id_match.group(1)}"
else:
print("Serial ID not found.")
return None
# Extract key-value pairs (str,str) from the settings block
settings_dict = dict(
re.findall(r"^\s*(\w):.*?\(([^()]*)\)", settings_block, re.MULTILINE)
)
return serial_id, settings_dict
def main() -> None:
# Get the serial ID and settings from the device
result = get_serial_id_and_settings()
if result is None:
print("Failed to retrieve serial ID and settings.")
return
serial_id, settings = result
# Show the results
print(f"Serial ID: {serial_id}")
for id, value in settings.items():
match id:
case "a":
print(f"Application ID: {value}")
# case "i":
# print(f"Logical ID: {value}")
# case "c":
# print(f"Channel: {value}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Explanation
Flow of Reading Output from Interactive Mode
- Reset the TWELITE
- Resetting brings the device back to its initial state for entering interactive mode. This reset is performed by controlling the reset pin on TWELITE R2/R3.
- Obtain the serial port instance
- Using
pyserial, obtain an instance for accessing serial I/O of TWELITE from the PC. Through this instance, you can send commands and read data.
- Using
- Input
+three times- By sending
+three times at fixed intervals (200–1000ms), TWELITE transitions into interactive mode. This method is the same as manual operation by the user.
- By sending
- Read output up to the line starting with
S:- In interactive mode, the line
S:appears after a series of configuration items. Reading up to this point ensures that all configuration contents are retrieved.
- In interactive mode, the line
- Reset the TWELITE
- After reading, reset again to return from interactive mode to normal operation.
with Tweliter(
type_filter=Tweliter.Type.TWELITE_R2 | Tweliter.Type.TWELITE_R3
) as liter:
# Reset the device
liter.reset_device()
# Get the serial port instance (pyserial)
ser = liter.get_serial_instance()
ser.timeout = 1.0
# Enter to the interactive mode
for _ in range(3):
ser.write("+")
time.sleep(0.3)
# Read the output
raw_output = ser.read_until(b"S:").decode("utf-8")
# Reset the device (Exit interactive mode)
liter.reset_device()
Flow of Interpreting Output from Interactive Mode
- Extract the line and the block enclosed by
---- Use
re.search(r"---(.*?)---(.*?)---", raw_output, re.DOTALL)to retrieve the full configuration info from the interactive mode output, divided into two parts:information_line(containing serial ID etc.), andsettings_block(listing configuration items).re.DOTALLenables matching across multiple lines.
- Use
- Extract the serial ID from the first line
- Use
re.search(r"SID=0x([0-9A-Fa-f]+)", information_line)to obtain the hexadecimal ID followingSID=0x, format it as a string like0x82010079. Both uppercase and lowercase hex digits are matched.
- Use
- Extract command ID and value pairs from the block
- Use
re.findall(r"^\s*(\w):.*?\(([^()]*)\)", settings_block, re.MULTILINE)to extract lines in the format likea: ... (value), retrieving the one-letter command ID and the value inside parentheses. Leading spaces and any characters after the colon are ignored.re.MULTILINEenables matching across multiple lines.
- Use
# Find the settings block in the output
filter_output = re.search(r"---(.*?)---(.*?)---", raw_output, re.DOTALL)
if filter_output:
information_line = filter_output.group(1)
settings_block = filter_output.group(2)
else:
print("No settings block found.")
return None
# Extract serial id from the information line
serial_id_match = re.search(r"SID=0x([0-9A-Fa-f]+)", information_line)
if serial_id_match:
serial_id = f"0x{serial_id_match.group(1)}"
else:
print("Serial ID not found.")
return None
# Extract key-value pairs (str,str) from the settings block
settings_dict = dict(
re.findall(r"^\s*(\w):.*?\(([^()]*)\)", settings_block, re.MULTILINE)
)
return serial_id, settings_dict
Reading Configuration Values and Changing Logical Device ID Using Python for Cue App
Here, we introduce a script that reads the serial ID and configuration values from a TWELITE device programmed with the Cue app App_Cue, via TWELITE R2/R3, and updates the logical device ID.
The tweliter module is used to identify TWELITE R2/R3, retrieve the serial port, and control the reset pin of TWELITE R2/R3.
pip install tweliter
Script
Using Python 3.12.
For the Cue app specifications, we enter interactive mode by pulling the SET pin low here.
Easy! Standard apps and serial communication apps may not support SET pin transition
Input + three times at 200-1000ms intervals as follows:
def enter_interactive_mode_manually(liter: Tweliter) -> None:
liter.reset_device()
ser = liter.get_serial_instance()
for _ in range(3):
ser.write("+")
time.sleep(0.3)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import time
import re
from tweliter import Tweliter # Mono Wireless module for TWELITE R devices
def revert_all_setttings(liter: Tweliter) -> None:
"""
Revert all settings
Args:
liter (Tweliter): Tweliter instance
"""
# Get the serial port instance (pyserial)
ser = liter.get_serial_instance()
ser.timeout = 1.0
# Set logical id
ser.write("R")
time.sleep(0.3)
ser.write("S")
def get_serial_id_and_settings(liter: Tweliter) -> tuple[str, dict[str, str]] | None:
"""
Get the serial ID and all settings
Args:
liter (Tweliter): Tweliter instance
Returns:
tuple[str, dict[str, str]] | None:
A tuple containing:
- str: the serial ID (e.g., "82010079")
- dict[str, str]: the settings dictionary (e.g., {'a': '0x67720103', ...})
Returns None if the device cannot be accessed or the output is invalid.
"""
# Get the serial port instance (pyserial)
ser = liter.get_serial_instance()
ser.timeout = 1.0
# Read the output
raw_output = ser.read_until(b"S:").decode("utf-8")
# Find the settings block in the output
filter_output = re.search(r"---(.*?)---(.*?)---", raw_output, re.DOTALL)
if filter_output:
information_line = filter_output.group(1)
settings_block = filter_output.group(2)
else:
print("No settings block found.")
return None
# Extract serial id from the information line
serial_id_match = re.search(r"SID=0x([0-9A-Fa-f]+)", information_line)
if serial_id_match:
serial_id = f"0x{serial_id_match.group(1)}"
else:
print("Serial ID not found.")
return None
# Extract key-value pairs (str,str) from the settings block
settings_dict = dict(
re.findall(r"^\s*(\w):.*?\(([^()]*)\)", settings_block, re.MULTILINE)
)
return serial_id, settings_dict
def set_logical_id(liter: Tweliter, lid: int) -> None:
"""
Set new logical id and save it
Args:
liter (Tweliter): Tweliter instance
lid (int): New logical id
"""
# Get the serial port instance (pyserial)
ser = liter.get_serial_instance()
ser.timeout = 1.0
# Set logical id
ser.write("i")
time.sleep(0.3)
ser.write(f"{lid}\r\n")
time.sleep(0.3)
ser.write("S")
def print_settings(settings: dict[str, str], select: list[str] | None = None) -> None:
"""
Print settings
Args:
settings (dict[str, str]): Settings dict
select (list[str] | None): List of IDs for selected entries. None to select all
"""
for id, value in settings.items():
if select is None or id in select:
match id:
case "a":
print(f"Application ID: {value}")
case "i":
print(f"Logical ID: {value}")
case "c":
print(f"Channel: {value}")
case "x":
print(f"Power / Retry: {value}")
case "b":
print(f"UART Baudrate: {value}")
case "B":
print(f"UART Options: {value}")
case "k":
print(f"Encryption Key: {value}")
case "o":
print(f"Option Bits: {value}")
case "t":
print(f"Transmission Interval: {value}")
case "p":
print(f"Sensor Parameters: {value}")
case _:
print(f"{id}: {value}")
def main() -> None:
"""
Main function
"""
lid_to_set = 25
try:
with Tweliter(
type_filter=Tweliter.Type.TWELITE_R2 | Tweliter.Type.TWELITE_R3
) as liter:
# Revert all settings
print("\nReverting to default settings...")
liter.enter_interactive_mode()
revert_all_setttings(liter)
# Get the serial ID and settings from the device
liter.enter_interactive_mode()
result = get_serial_id_and_settings(liter)
if result is None:
print("Failed to get serial ID and settings.")
return
serial_id, settings = result
print(f"\nCurrent settings for the device {serial_id}:")
print_settings(settings)
# Set logical ID
print(
f"\nModifying Logical ID {settings["i"]} to {lid_to_set}=0x{lid_to_set:02x}..."
)
set_logical_id(liter, lid_to_set)
# Get updated setttings
liter.enter_interactive_mode()
result = get_serial_id_and_settings(liter)
if result is None:
print("Failed to get serial ID and settings.")
return
serial_id, settings = result
print(f"\nUpdated setting(s) for the device {serial_id}:")
print_settings(settings, select=["i"])
# Reset the device (Exit interactive mode)
liter.reset_device()
except IOError as e:
print(f"Couldn't open the device {e}")
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
When you run the script, it changes the logical device ID to 25 as shown in the following example:
python modify_app_cue_settings.py
Using TWE-Lite-R R27BESFJ @ ftdi://::R27BESFJ/1
Reverting to default settings...
Current settings for the device 0x8201872b:
Application ID: 0x67720102
Logical ID: --
Channel: 18
Power / Retry: 13
UART Baudrate: 38400
UART Options: 8N1
Encryption Key: 0xA5A5A5A5
Option Bits: 0x00000001
Transmission Interval: 5
Sensor Parameters: 0x00000000
Modifying Logical ID -- to 25=0x19...
Updated setting(s) for the device 0x8201872b:
Logical ID: 25=0x19
Explanation
Process for Reading Configuration Values
- Get the serial port instance
- Use
get_serial_instance()to obtain the serial port instance.
- Use
- Read the string from the serial port up to
S:which contains the save command description- In interactive mode, after the configuration values are displayed, the save command description
S:appears. By reading up to this point, you can retrieve all configuration content.
- In interactive mode, after the configuration values are displayed, the save command description
- Extract the first line and the block enclosed by
---- Use
re.search(r"---(.*?)---(.*?)---", raw_output, re.DOTALL)to extract the interactive mode output into two parts: the first capture group is the information line (information_line) containing the serial ID, and the next group is the settings block (settings_block) containing the configuration items.re.DOTALLenables full-text search including newlines.
- Use
- Extract the serial ID from the first line
- Use
re.search(r"SID=0x([0-9A-Fa-f]+)", information_line)to retrieve the hexadecimal ID value followingSID=0x(e.g.,82010079) and format it as a string like0x82010079. Hexadecimal digits are extracted regardless of case.
- Use
- Extract command ID and value pairs from the block
- Use
re.findall(r"^\s*(\w):.*?\(([^()]*)\)", settings_block, re.MULTILINE)to extract the command ID (single character) and the value within parentheses from lines in the formata: ... (value). Leading spaces and any characters after the colon are skipped, extracting only the first parenthesized value found.re.MULTILINEenables matching across multiple lines.
- Use
# Get the serial port instance (pyserial)
ser = liter.get_serial_instance()
ser.timeout = 1.0
# Read the output
raw_output = ser.read_until(b"S:").decode("utf-8")
# Find the settings block in the output
filter_output = re.search(r"---(.*?)---(.*?)---", raw_output, re.DOTALL)
if filter_output:
information_line = filter_output.group(1)
settings_block = filter_output.group(2)
else:
print("No settings block found.")
return None
# Extract serial id from the information line
serial_id_match = re.search(r"SID=0x([0-9A-Fa-f]+)", information_line)
if serial_id_match:
serial_id = f"0x{serial_id_match.group(1)}"
else:
print("Serial ID not found.")
return None
# Extract key-value pairs (str,str) from the settings block
settings_dict = dict(
re.findall(r"^\s*(\w):.*?\(([^()]*)\)", settings_block, re.MULTILINE)
)
return serial_id, settings_dict